Page 568 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 568
544 Initiation & Intensification of Insulin Therapy in T2DM
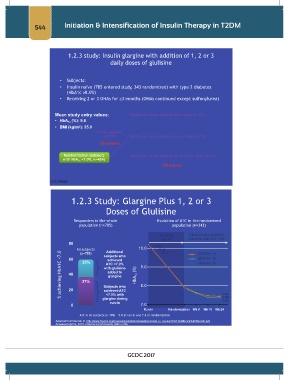
1.2.3 study: Insulin glargine with addition of 1, 2 or 3
daily doses of glulisine
• Subjects:
• Insulin naïve (785 entered study, 343 randomized) with type 2 diabetes
(HbA1c ≥8.0%)
• Receiving 2 or 3 OHAs for ≥3 months (OHAs continued except sulfonylurea)
Mean study entry values: Additional insulin glulisine once daily (n=115)
• HbA 1c (%): 9.8
• BMI (kg/m ): 35.0
2
Insulin glargine
(n=785) Additional insulin glulisine twice daily (n=113)
14 weeks
Randomization (subjects Additional insulin glulisine three times daily (n=115)
with HbA 1c >7.0%, n=434)
24 weeks
(1.2.3 study)
1.2.3 Study: Glargine Plus 1, 2 or 3
Doses of Glulisine
Responders in the whole Evolution of A1C in the randomized
population (n=785) population (n=343)
Glargine Glargine plus glulisine
(alone) (patients with A1C >7%)
80 10.19
All subjects subjects who 10.0 10.19 Glulisine 1x
Additional
10.16
% achieving HbA1C <7.0 40 37% with glulisine HbA 1c (%) 9.0 Glulisine 3x
(n=785)
Glulisine 2x
60
achieved
23%
A1C <7.0%
added to
glargine
8.0
Subjects who
20
achievedA1C
<7.0% with
7.40
glargine during
7.29
run-in 7.44
0 7.0
Run in Randomization Wk 8 Wk 16 Wk 24
A1C in all subjects (n=785) = 9.8 at run-in and 7.3 at randomization
Adapted from Raccah D. http://www.fesemi.org/grupos/obesidad/noticias/ponencias_iv_reunion/Prof.%20Denis%20Raccah.pdf.
Accessed April 9, 2010. Cited as sanofi aventis, data on file.
GCDC 2017