Page 581 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 581
Sulfonylureas and Cardiovascular Mortality? 557
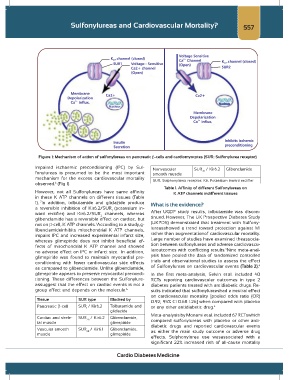
Figure 1: Mechanism of action of sulfonylureas on pancreatic β-cells and cardiomyocytes (SUR: Sulfonylurea receptor)
Impaired ischaemic preconditioning (IPC) by Sul- Nonvascular SUR / Kir6.2 Glibenclamide
fonylureas is presumed to be the most important smooth muscle 2B
mechanism for the excess cardiovascular mortality SUR, Sulphonylurea receptor; Kir, Potassium inward rectifier
observed. (Fig 1)
6
Table 1. Affinity of different Sulfonylureas on
However, not all Sulfonylureas have same affinity K ATP channels indifferent tissues
in these K ATP channels on different tissues (Table
1). In addition, tolbutamide and gliclazide produce What is the evidence?
7
a reversible inhibition of Kir6.2/SUR (potassium in-
1
ward rectifier) and Kir6.2/SUR channels, whereas After UGDP study results, tolbutamide was discon-
2
glibenclamide has a reversible effect on cardiac, but tinued. However, The UK Prospective Diabetes Study
not on β-cell, K ATP channels. According to a study,g- (UKPDS) demonstrated that treatment with Sulfony-
7
libenclamideinhibits mitochondrial K ATP channels, lureasshowed a trend toward protection against MI
impairs IPC and increased experimental infarct size, rather than augmentationof cardiovascular mortality.
whereas glimepiride does not inhibit beneficial ef- Large number of studies have examined theassocia-
fects of mitochondrial K ATP channel and showed tion between sulfonylureas and adverse cardiovascu-
4
no adverse effect on IPC or infarct size. In addition, laroutcomes with conflicting results. Nine meta-anal-
glimepiride was found to maintain myocardial pre- ysis have pooled the data of randomized controlled
conditioning with fewer cardiovascular side effects trials and observational studies to assess the effect
4
as compared to glibenclamide. Unlike glibenclamide, of Sulfonylureas on cardiovascular events (Table 2).
glimepiride appears to preserve myocardial precondi- In the first meta-analysis, Selvin et al. included 40
tioning. These differences between the Sulfonylure- RCTs reporting cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
assuggest that the effect on cardiac events is not a diabetes patients treated with antidiabetic drugs. Re-
group effect and depends on the molecule. 6 sults indicated that sulfonylureashad a neutral effect
on cardiovascular mortality [pooled odds ratio (OR)
Tissue SUR type Blocked by
0.92; 95% CI 0.68–1.26] when compared with placebo
Pancreatic β-cell SUR / Kir6.2 Tolbutamide and or any other antidiabetic drug. 4
1
gliclazide
Meta-analysis by Monami et al. included 67 RCTswhich
Cardiac and skele- SUR / Kir6.2 Glibenclamide,
2A
tal muscle glimepiride compared sulfonylureas with placebo or other anti-
diabetic drugs and reported cardiovascular events
Vascular smooth SUR / Kir6.1 Glibenclamide, as either the main study outcome or adverse drug
2B
muscle glimepiride
effects. Sulphonylurea use wasassociated with a
significant 22% increased risk of all-cause mortality
Cardio Diabetes Medicine