Page 21 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 21
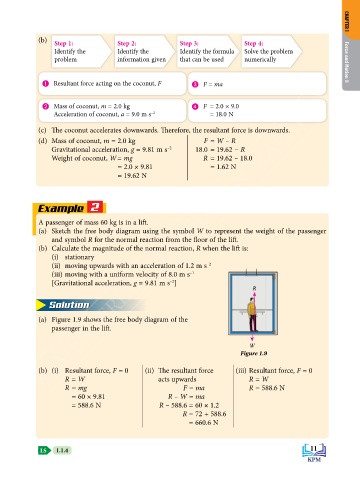
(b) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Step 4: CHAPTER 1
Identify the Identify the Identify the formula Solve the problem
problem information given that can be used numerically Force and Motion II
Resultant force acting on the coconut, F F = ma
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
Mass of coconut, m = 2.0 kg F = 2.0 × 9.0
Acceleration of coconut, a = 9.0 m s –2 = 18.0 N
(c) The coconut accelerates downwards. Therefore, the resultant force is downwards.
(d) Mass of coconut, m = 2.0 kg F = W – R
Gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m s –2 18.0 = 19.62 − R
Weight of coconut, W = mg R = 19.62 – 18.0
= 2.0 × 9.81 = 1.62 N
= 19.62 N
Example 2
A passenger of mass 60 kg is in a lift.
(a) Sketch the free body diagram using the symbol W to represent the weight of the passenger
and symbol R for the normal reaction from the floor of the lift.
(b) Calculate the magnitude of the normal reaction, R when the lift is:
(i) stationary
(ii) moving upwards with an acceleration of 1.2 m s –2
(iii) moving with a uniform velocity of 8.0 m s –1
[Gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m s ]
–2
R
Solution
(a) Figure 1.9 shows the free body diagram of the
passenger in the lift.
W
Figure 1.9
(b) (i) Resultant force, F = 0 (ii) The resultant force (iii) Resultant force, F = 0
R = W acts upwards R = W
R = mg F = ma R = 588.6 N
= 60 × 9.81 R – W = ma
= 588.6 N R – 588.6 = 60 × 1.2
R = 72 + 588.6
= 660.6 N
LS 1.1.4 11