Page 18 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 18
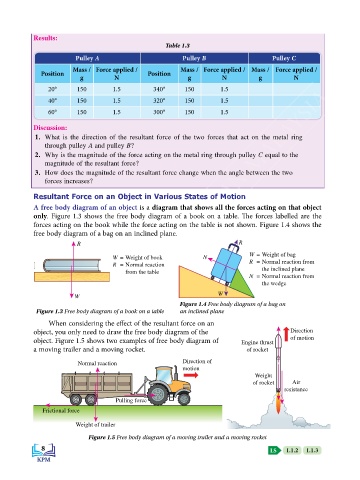
Results:
Table 1.3
Pulley A Pulley B Pulley C
Mass / Force applied / Mass / Force applied / Mass / Force applied /
Position Position
g N g N g N
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
20° 150 1.5 340° 150 1.5
40° 150 1.5 320° 150 1.5
60° 150 1.5 300° 150 1.5
Discussion:
1. What is the direction of the resultant force of the two forces that act on the metal ring
through pulley A and pulley B?
2. Why is the magnitude of the force acting on the metal ring through pulley C equal to the
magnitude of the resultant force?
3. How does the magnitude of the resultant force change when the angle between the two
forces increases?
Resultant Force on an Object in Various States of Motion
A free body diagram of an object is a diagram that shows all the forces acting on that object
only. Figure 1.3 shows the free body diagram of a book on a table. The forces labelled are the
forces acting on the book while the force acting on the table is not shown. Figure 1.4 shows the
free body diagram of a bag on an inclined plane.
R R
W = Weight of bag
W = Weight of book N
R = Normal reaction R = Normal reaction from
from the table the inclined plane
N = Normal reaction from
the wedge
W W
Figure 1.4 Free body diagram of a bag on
Figure 1.3 Free body diagram of a book on a table an inclined plane
When considering the effect of the resultant force on an
object, you only need to draw the free body diagram of the Direction
object. Figure 1.5 shows two examples of free body diagram of Engine thrust of motion
a moving trailer and a moving rocket. of rocket
Normal reaction Direction of
motion
Weight
of rocket Air
resistance
Pulling force
Frictional force
Weight of trailer
Figure 1.5 Free body diagram of a moving trailer and a moving rocket
8 LS 1.1.2 1.1.3