Page 146 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 146
Chapter 3 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL CARDIAC AND VASCULAR NEEDS 131
The risk factors of HF include hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol levels,
obesity, sleep apnea, and a family history of cardiomegaly.
A decrease in cardiac output from HF results in complex hemodynamic and
neurohormonal changes. The stress on the heart from structural/functional abnor-
malities results in a decreased CO. This increases circulating catecholamines, chiefly
epinephrine. Epinephrine increases the heart rate and the oxygen consumption,
resulting in an increase in demand on the heart, which stresses the heart further.
Heart failure can happen suddenly or acutely in the instance of a patient
having a fast tachy rhythm. It can also be slow and insidious in onset as with a
patient having slowly rising hypertension. Compensation for heart failure
includes the following mechanisms:
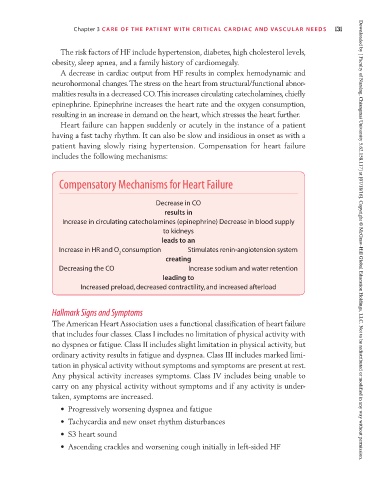
Compensatory Mechanisms for Heart Failure
Decrease in CO
results in
Increase in circulating catecholamines (epinephrine) Decrease in blood supply
to kidneys
leads to an Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Increase in HR and O consumption Stimulates renin-angiotension system
2
creating
Decreasing the CO Increase sodium and water retention
leading to
Increased preload, decreased contractility, and increased afterload
Hallmark Signs and Symptoms
The American Heart Association uses a functional classification of heart failure
that includes four classes. Class I includes no limitation of physical activity with
no dyspnea or fatigue. Class II includes slight limitation in physical activity, but
ordinary activity results in fatigue and dyspnea. Class III includes marked limi-
tation in physical activity without symptoms and symptoms are present at rest.
Any physical activity increases symptoms. Class IV includes being unable to
carry on any physical activity without symptoms and if any activity is under-
taken, symptoms are increased.
• Progressively worsening dyspnea and fatigue
• Tachycardia and new onset rhythm disturbances
• S3 heart sound
• Ascending crackles and worsening cough initially in left-sided HF