Page 147 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 147
132 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
• Drop in the O saturation levels in right-sided HF
2
• Hypotension
• Decreased urinary output
• Increased weight gain
• Reduction of CO elevated PAWP
• Elevated CVP if the patient has right-sided HF alone OR right AND left-
sided HF
The signs and symptoms of HF can be further broken down into right- and
left-sided heart failure. Left-sided HF is considered much worse as it affects
oxygenation of the body and can lead to cardiogenic shock (see Table 3–16).
Prognosis
This is an insidious disease with over 5 million Americans living with HF. Thirty
to sixty percent of patients are readmitted within 6 months of initial diagnosis
and hospitalization.
Interpreting Test Results
ECGs are done to look for cardiac ischemia or conduction problems that could Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
cause HF. Rhythm disturbances can include many forms of dysrhythmias
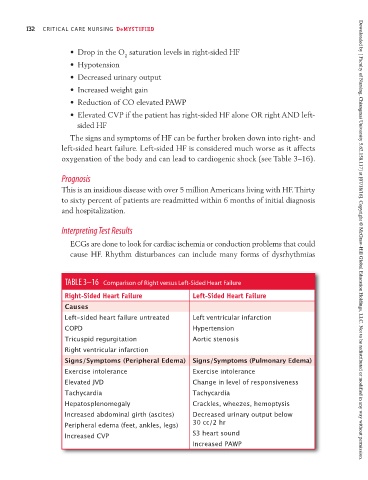
TABLE 3–16 Comparison of Right versus Left-Sided Heart Failure
Right-Sided Heart Failure Left-Sided Heart Failure
Causes
Left-sided heart failure untreated Left ventricular infarction
COPD Hypertension
Tricuspid regurgitation Aortic stenosis
Right ventricular infarction
Signs/Symptoms (Peripheral Edema) Signs/Symptoms (Pulmonary Edema)
Exercise intolerance Exercise intolerance
Elevated JVD Change in level of responsiveness
Tachycardia Tachycardia
Hepatosplenomegaly Crackles, wheezes, hemoptysis
Increased abdominal girth (ascites) Decreased urinary output below
Peripheral edema (feet, ankles, legs) 30 cc/2 hr
Increased CVP S3 heart sound
Increased PAWP