Page 233 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 233
218 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
Many other terms are used to describe the LOC and the critical care nurse
must be familiar with these terms. Table 5–4 describes commonly used general
terms for LOC.
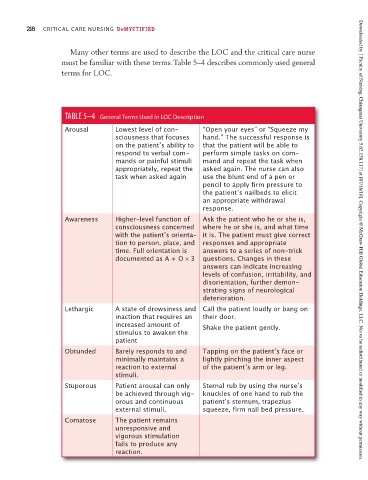
TABLE 5–4 General Terms Used in LOC Description
Arousal Lowest level of con- “Open your eyes” or “Squeeze my
sciousness that focuses hand.” The successful response is
on the patientʼs ability to that the patient will be able to
respond to verbal com- perform simple tasks on com-
mands or painful stimuli mand and repeat the task when
appropriately, repeat the asked again. The nurse can also
task when asked again use the blunt end of a pen or
pencil to apply firm pressure to
the patientʼs nailbeds to elicit
an appropriate withdrawal
response.
Awareness Higher-level function of Ask the patient who he or she is,
consciousness concerned where he or she is, and what time
with the patientʼs orienta- it is. The patient must give correct
tion to person, place, and responses and appropriate Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
time. Full orientation is answers to a series of non-trick
documented as A + O × 3 questions. Changes in these
answers can indicate increasing
levels of confusion, irritability, and
disorientation, further demon-
strating signs of neurological
deterioration.
Lethargic A state of drowsiness and Call the patient loudly or bang on
inaction that requires an their door.
increased amount of Shake the patient gently.
stimulus to awaken the
patient
Obtunded Barely responds to and Tapping on the patientʼs face or
minimally maintains a lightly pinching the inner aspect
reaction to external of the patientʼs arm or leg.
stimuli.
Stuporous Patient arousal can only Sternal rub by using the nurseʼs
be achieved through vig- knuckles of one hand to rub the
orous and continuous patientʼs sternum, trapezius
external stimuli. squeeze, firm nail bed pressure.
Comatose The patient remains
unresponsive and
vigorous stimulation
fails to produce any
reaction.