Page 229 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 229
214 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
barrier prevents some chemotherapeutic medications from entering the CNS, so
those medications require another route of administration such as intrathecal.
The CSF is a clear, odorless, and colorless fluid that forms in the ventricles of
the brain and flows in the ventricles of the brain, the subarachnoid space, and the
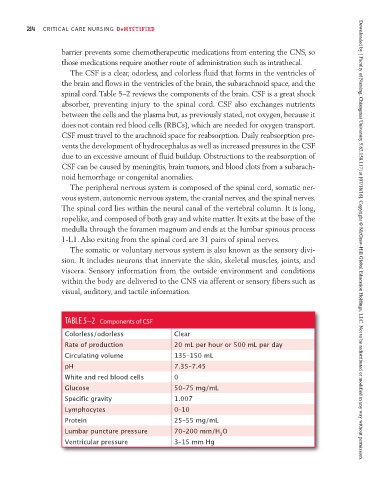
spinal cord. Table 5–2 reviews the components of the brain. CSF is a great shock
absorber, preventing injury to the spinal cord. CSF also exchanges nutrients
between the cells and the plasma but, as previously stated, not oxygen, because it
does not contain red blood cells (RBCs), which are needed for oxygen transport.
CSF must travel to the arachnoid space for reabsorption. Daily reabsorption pre-
vents the development of hydrocephalus as well as increased pressures in the CSF
due to an excessive amount of fluid buildup. Obstructions to the reabsorption of
CSF can be caused by meningitis, brain tumors, and blood clots from a subarach-
noid hemorrhage or congenital anomalies.
The peripheral nervous system is composed of the spinal cord, somatic ner-
vous system, autonomic nervous system, the cranial nerves, and the spinal nerves.
The spinal cord lies within the neural canal of the vertebral column. It is long,
ropelike, and composed of both gray and white matter. It exits at the base of the
medulla through the foramen magnum and ends at the lumbar spinous process
1-L1. Also exiting from the spinal cord are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
The somatic or voluntary nervous system is also known as the sensory divi-
sion. It includes neurons that innervate the skin, skeletal muscles, joints, and
viscera. Sensory information from the outside environment and conditions
within the body are delivered to the CNS via afferent or sensory fibers such as
visual, auditory, and tactile information.
TABLE 5–2 Components of CSF
Colorless/odorless Clear
Rate of production 20 mL per hour or 500 mL per day
Circulating volume 135–150 mL
pH 7.35–7.45
White and red blood cells 0
Glucose 50–75 mg/mL
Specific gravity 1.007
Lymphocytes 0–10
Protein 25–55 mg/mL
Lumbar puncture pressure 70–200 mm/H O
2
Ventricular pressure 3–15 mm Hg