Page 396 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 396
Chapter 8 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RENAL NEEDS 381
Like PD, CRRT uses the principles of diffusion and osmosis to remove fluid and
waste products from the patient’s system. Unlike HD and PD, it is much slower
and is administered over a longer period of time. Because body changes occur
at a much slower rate, CRRT can be used if the patient is hemodynamically
unstable, making it a clear choice in many shocky patients. It can be done over
24 hours until the patient is stabilized and can tolerate other forms of dialysis
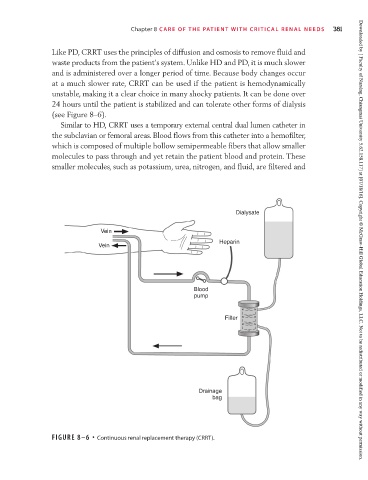
(see Figure 8–6).
Similar to HD, CRRT uses a temporary external central dual lumen catheter in
the subclavian or femoral areas. Blood flows from this catheter into a hemofilter,
which is composed of multiple hollow semipermeable fibers that allow smaller
molecules to pass through and yet retain the patient blood and protein. These
smaller molecules, such as potassium, urea, nitrogen, and fluid, are filtered and
Dialysate
Vein
Heparin Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Vein
Blood
pump
Filter
Drainage
bag
FIGURE 8–6 • Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT).