Page 400 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 400
Chapter 8 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RENAL NEEDS 385
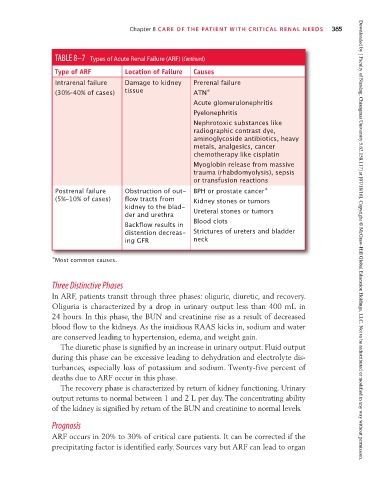
TABLE 8–7 Types of Acute Renal Failure (ARF) (Continued)
Type of ARF Location of Failure Causes
Intrarenal failure Damage to kidney Prerenal failure
(30%–40% of cases) tissue ATN ∗
Acute glomerulonephritis
Pyelonephritis
Nephrotoxic substances like
radiographic contrast dye,
aminoglycoside antibiotics, heavy
metals, analgesics, cancer
chemotherapy like cisplatin
Myoglobin release from massive
trauma (rhabdomyolysis), sepsis
or transfusion reactions
Postrenal failure Obstruction of out- BPH or prostate cancer ∗
(5%–10% of cases) flow tracts from Kidney stones or tumors
kidney to the blad-
der and urethra Ureteral stones or tumors
Blood clots
Backflow results in
distention decreas- Strictures of ureters and bladder
ing GFR neck Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
∗ Most common causes.
Three Distinctive Phases
In ARF, patients transit through three phases: oliguric, diuretic, and recovery.
Oliguria is characterized by a drop in urinary output less than 400 mL in
24 hours. In this phase, the BUN and creatinine rise as a result of decreased
blood flow to the kidneys. As the insidious RAAS kicks in, sodium and water
are conserved leading to hypertension, edema, and weight gain.
The diuretic phase is signified by an increase in urinary output. Fluid output
during this phase can be excessive leading to dehydration and electrolyte dis-
turbances, especially loss of potassium and sodium. Twenty-five percent of
deaths due to ARF occur in this phase.
The recovery phase is characterized by return of kidney functioning. Urinary
output returns to normal between 1 and 2 L per day. The concentrating ability
of the kidney is signified by return of the BUN and creatinine to normal levels.
Prognosis
ARF occurs in 20% to 30% of critical care patients. It can be corrected if the
precipitating factor is identified early. Sources vary but ARF can lead to organ