Page 397 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 397
382 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
removed from the body into a drainage bag. The bag is drained according to
institutional protocols, not unlike PD, and a tally is kept of how much fluid the
CRRT has removed from the patient.
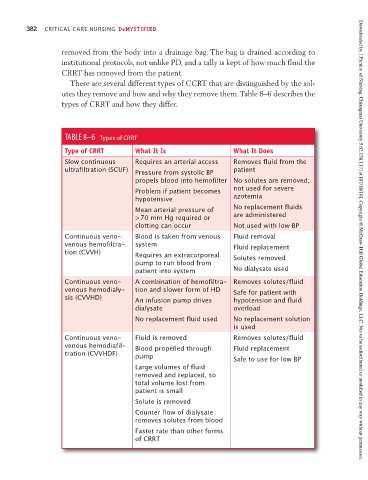
There are several different types of CCRT that are distinguished by the sol-
utes they remove and how and why they remove them. Table 8–6 describes the
types of CRRT and how they differ.
TABLE 8–6 Types of CRRT
Type of CRRT What It Is What It Does
Slow continuous Requires an arterial access Removes fluid from the
ultrafiltration (SCUF) Pressure from systolic BP patient
propels blood into hemofilter No solutes are removed;
Problem if patient becomes not used for severe
hypotensive azotemia
Mean arterial pressure of No replacement fluids
>70 mm Hg required or are administered
clotting can occur Not used with low BP
Continuous veno- Blood is taken from venous Fluid removal
venous hemofiltra- system Fluid replacement Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
tion (CVVH) Requires an extracorporeal
pump to run blood from Solutes removed
patient into system No dialysate used
Continuous veno- A combination of hemofiltra- Removes solutes/fluid
venous hemodialy- tion and slower form of HD Safe for patient with
sis (CVVHD) An infusion pump drives hypotension and fluid
dialysate overload
No replacement fluid used No replacement solution
is used
Continuous veno- Fluid is removed Removes solutes/fluid
venous hemodiafil- Blood propelled through Fluid replacement
tration (CVVHDF)
pump Safe to use for low BP
Large volumes of fluid
removed and replaced, so
total volume lost from
patient is small
Solute is removed
Counter flow of dialysate
removes solutes from blood
Faster rate than other forms
of CRRT