Page 42 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 42
Chapter 2 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RESPIRATORY NEEDS 27
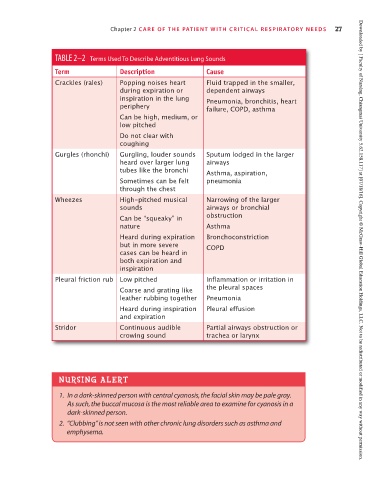
TABLE 2–2 Terms Used To Describe Adventitious Lung Sounds
Term Description Cause
Crackles (rales) Popping noises heart Fluid trapped in the smaller,
during expiration or dependent airways
inspiration in the lung Pneumonia, bronchitis, heart
periphery failure, COPD, asthma
Can be high, medium, or
low pitched
Do not clear with
coughing
Gurgles (rhonchi) Gurgling, louder sounds Sputum lodged in the larger
heard over larger lung airways
tubes like the bronchi Asthma, aspiration,
Sometimes can be felt pneumonia
through the chest
Wheezes High-pitched musical Narrowing of the larger
sounds airways or bronchial
Can be “squeaky” in obstruction
nature Asthma
Heard during expiration Bronchoconstriction
but in more severe COPD Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
cases can be heard in
both expiration and
inspiration
Pleural friction rub Low pitched Inflammation or irritation in
Coarse and grating like the pleural spaces
leather rubbing together Pneumonia
Heard during inspiration Pleural effusion
and expiration
Stridor Continuous audible Partial airways obstruction or
crowing sound trachea or larynx
NURSING ALERT
1. In a dark-skinned person with central cyanosis, the facial skin may be pale gray.
As such, the buccal mucosa is the most reliable area to examine for cyanosis in a
dark-skinned person.
2. “Clubbing” is not seen with other chronic lung disorders such as asthma and
emphysema.