Page 54 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 54
Chapter 2 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RESPIRATORY NEEDS 39
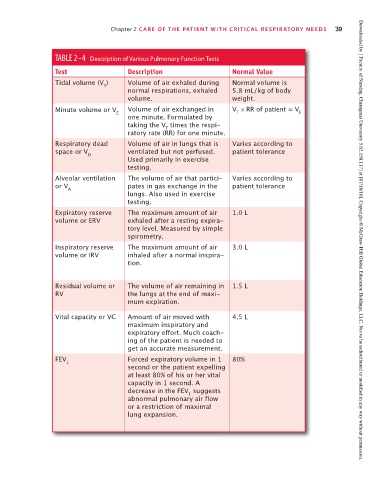
TABLE 2–4 Description of Various Pulmonary Function Tests
Test Description Normal Value
Tidal volume (V ) Volume of air exhaled during Normal volume is
T
normal respirations, exhaled 5.8 mL/kg of body
volume. weight.
Minute volume or V Volume of air exchanged in V × RR of patient = V
E T E
one minute. Formulated by
taking the V times the respi-
T
ratory rate (RR) for one minute.
Respiratory dead Volume of air in lungs that is Varies according to
space or V ventilated but not perfused. patient tolerance
D
Used primarily in exercise
testing.
Alveolar ventilation The volume of air that partici- Varies according to
or V pates in gas exchange in the patient tolerance
A
lungs. Also used in exercise
testing.
Expiratory reserve The maximum amount of air 1.0 L
volume or ERV exhaled after a resting expira-
tory level. Measured by simple
spirometry. Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Inspiratory reserve The maximum amount of air 3.0 L
volume or IRV inhaled after a normal inspira-
tion.
Residual volume or The volume of air remaining in 1.5 L
RV the lungs at the end of maxi-
mum expiration.
Vital capacity or VC Amount of air moved with 4.5 L
maximum inspiratory and
expiratory effort. Much coach-
ing of the patient is needed to
get an accurate measurement.
FEV Forced expiratory volume in 1 80%
1
second or the patient expelling
at least 80% of his or her vital
capacity in 1 second. A
decrease in the FEV suggests
1
abnormal pulmonary air flow
or a restriction of maximal
lung expansion.