Page 55 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 55
40 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
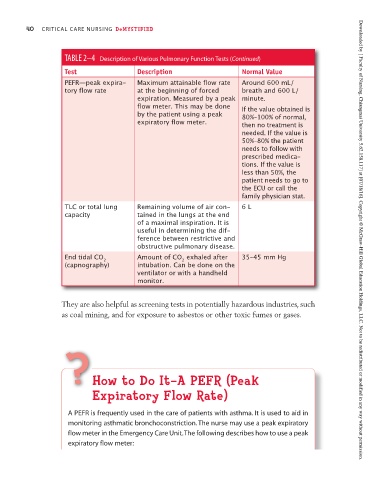
TABLE 2–4 Description of Various Pulmonary Function Tests (Continued)
Test Description Normal Value
PEFR—peak expira- Maximum attainable flow rate Around 600 mL/
tory flow rate at the beginning of forced breath and 600 L/
expiration. Measured by a peak minute.
flow meter. This may be done If the value obtained is
by the patient using a peak 80%–100% of normal,
expiratory flow meter. then no treatment is
needed. If the value is
50%–80% the patient
needs to follow with
prescribed medica-
tions. If the value is
less than 50%, the
patient needs to go to
the ECU or call the
family physician stat.
TLC or total lung Remaining volume of air con- 6 L
capacity tained in the lungs at the end
of a maximal inspiration. It is
useful in determining the dif-
ference between restrictive and Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
obstructive pulmonary disease.
End tidal CO 2 Amount of CO exhaled after 35–45 mm Hg
2
(capnography) intubation. Can be done on the
ventilator or with a handheld
monitor.
They are also helpful as screening tests in potentially hazardous industries, such
as coal mining, and for exposure to asbestos or other toxic fumes or gases.
H ? How to Do It—A PEFR (Peak
t—
P
o D
o I
o
A
w t
Expiratory Flow Rate)
Expiratory Flow
f
e o
e
quentl
r
A PEFR is frequently used in the care of patients with asthma. It is used to aid in
f
A
pa
PEFR is
used in the car
y
onstric
monitoring asthmatic bronchoconstriction. The nurse may use a peak expiratory
monit
tion
oc
n
c
matic
b
ro
ring ast
o
h
h
genc
f flow meter in the Emergency Care Unit. The following describes how to use a peak
er in the Emer
he
y
e Unit.
ar
C
w met
T
lo
expiratory flow meter::
e xpirat or y flo w met er