Page 46 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 46
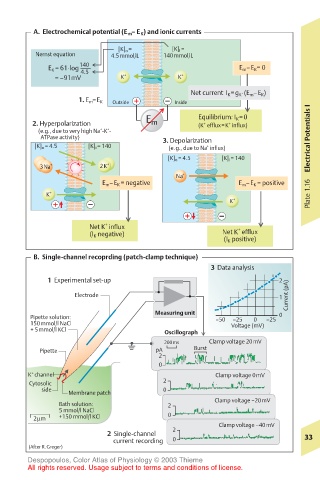
A. Electrochemical potential (E m – E K ) and ionic currents
[K] o = [K] i =
Nernst equation 4.5mmol/L 140mmol/L
140
E K = 61·log –––– E m –E K = 0
4.5
= –91mV K + K +
Net current I K =g K ·(E m –E K )
1. E m =E K Outside Inside
E Equilibrium: I K =0
2. Hyperpolarization m (K efflux=K influx)
+
+
(e.g., due to very high Na -K - +
+
ATPase activity) 3. Depolarization Electrical Potentials I
[K] o = 4.5 [K] i = 140 (e.g., due to Na influx)
+
[K] o = 4.5 [K] i = 140
3Na + 2K +
Na +
E m –E K = negative E m –E K = positive
K + Plate 1.16
K +
+
Net K influx +
(I K negative) Net K efflux
(I K positive)
B. Single-channel recoprding (patch-clamp technique)
3 Data analysis
1 Experimental set-up 2
Current (pA) 1
Electrode
Measuring unit
Pipette solution: –50 –25 0 –25 0
150mmol/l NaCl Voltage (mV)
+ 5mmol/l KCl Oscillograph
200ms Clamp voltage 20mV
Pipette pA Burst
2
0
+
K channel Clamp voltage 0mV
Cytosolic 2
side 0
Membrane patch
Clamp voltage –20mV
Bath solution: 2
5 mmol/l NaCl
2µm +150 mmol/l KCl 0
Clamp voltage –40mV
2
2 Single-channel 33
33
current recording 0
(After R.Greger)
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.