Page 84 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 84
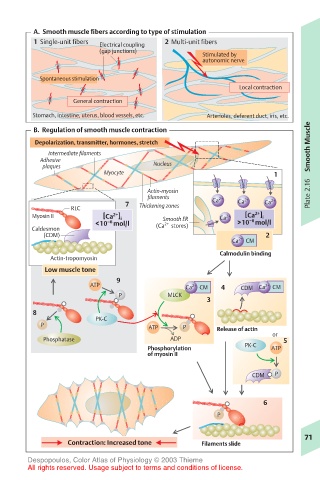
A. Smooth muscle fibers according to type of stimulation
1 Single-unit fibers Electrical coupling 2 Multi-unit fibers
(gap junctions)
Stimulated by
autonomic nerve
Spontaneous stimulation
Local contraction
General contraction
Stomach, intestine, uterus, blood vessels, etc. Arterioles, deferent duct, iris, etc.
B. Regulation of smooth muscle contraction
Depolarization, transmitter, hormones, stretch Smooth Muscle
Intermediate filaments
Adhesive
plaques Nucleus
Myocyte 1
Actin-myosin
filaments Ca 2+ 2+ 2+ Plate 2.16
7 Thickening zones Ca Ca
RLC
2+
2+
Myosin II [Ca ] i Smooth ER Ca 2+ [Ca ] i
–6
–6
<10 mol/l (Ca stores) >10 mol/l
2+
Caldesmon
(CDM) 2
Ca 2+ CM
Calmodulin binding
Actin-tropomyosin
Low muscle tone
9
ATP Ca 2+ CM 4 CDM Ca 2+ CM
P MLCK
3
8
PK-C
P ATP P Release of actin
or
Phosphatase ADP 5
Phosphorylation PK-C ATP
of myosin II
CDM P
6
P
71
Contraction: Increased tone Filaments slide
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.