Page 707 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 707
526 PART 4: Pulmonary Disorders
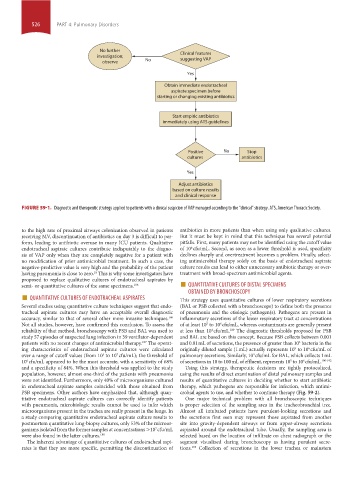
No further
investigation; Clinical features
suggesting VAP
observe No
Yes
Obtain immediate endotracheal
aspirate specimen before
starting or changing existing antibiotics
Start empiric antibiotics
immediately using ATS guidelines
Positive No Stop
cultures antibiotics
Yes
Adjust antibiotics
based on culture results
and clinical response
FIGURE 59-1. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategy applied to patients with a clinical suspicion of VAP managed according to the “clinical” strategy. ATS, American Thoracic Society.
to the high rate of proximal airways colonization observed in patients antibiotics in more patients than when using only qualitative cultures.
receiving MV, discontinuation of antibiotics on day 3 is difficult to per- But it must be kept in mind that this technique has several potential
form, leading to antibiotic overuse in many ICU patients. Qualitative pitfalls. First, many patients may not be identified using the cutoff value
6
endotracheal aspirate cultures contribute indisputably to the diagno- of 10 cfu/mL. Second, as soon as a lower threshold is used, specificity
sis of VAP only when they are completely negative for a patient with declines sharply and overtreatment becomes a problem. Finally, select-
no modification of prior antimicrobial treatment. In such a case, the ing antimicrobial therapy solely on the basis of endotracheal aspirate
negative-predictive value is very high and the probability of the patient culture results can lead to either unnecessary antibiotic therapy or over-
having pneumonia is close to zero. This is why some investigators have treatment with broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents.
18
proposed to replace qualitative cultures of endotracheal aspirates by ■
semi- or quantitative cultures of the same specimens. 186 QUANTITATIVE CULTURES OF DISTAL SPECIMENS
■ QUANTITATIVE CULTURES OF ENDOTRACHEAL ASPIRATES This strategy uses quantitative cultures of lower respiratory secretions
OBTAINED BY BRONCHOSCOPY
Several studies using quantitative culture techniques suggest that endo- (BAL or PSB collected with a bronchoscope) to define both the presence
tracheal aspirate cultures may have an acceptable overall diagnostic of pneumonia and the etiologic pathogen(s). Pathogens are present in
accuracy, similar to that of several other more invasive techniques. inflammatory secretions of the lower respiratory tract at concentrations
186
Not all studies, however, have confirmed this conclusion. To assess the of at least 10 to 10 cfu/mL, whereas contaminants are generally present
5
6
reliability of that method, bronchoscopy with PSB and BAL was used to at less than 10 cfu/mL. The diagnostic thresholds proposed for PSB
189
4
study 57 episodes of suspected lung infection in 39 ventilator-dependent and BAL are based on this concept. Because PSB collects between 0.001
patients with no recent changes of antimicrobial therapy. The operat- and 0.01 mL of secretions, the presence of greater than 10 bacteria in the
187
3
ing characteristics of endotracheal aspirate cultures were calculated originally diluted sample (1 mL) actually represents 10 to 10 cfu/mL of
5
6
over a range of cutoff values (from 10 to 10 cfu/mL); the threshold of pulmonary secretions. Similarly, 10 cfu/mL for BAL, which collects 1 mL
7
4
3
10 cfu/mL appeared to be the most accurate, with a sensitivity of 68% of secretions in 10 to 100 mL of effluent, represents 10 to 10 cfu/mL. 190-192
5
6
6
and a specificity of 84%. When this threshold was applied to the study Using this strategy, therapeutic decisions are tightly protocolized,
population, however, almost one-third of the patients with pneumonia using the results of direct examination of distal pulmonary samples and
were not identified. Furthermore, only 40% of microorganisms cultured results of quantitative cultures in deciding whether to start antibiotic
in endotracheal aspirate samples coincided with those obtained from therapy, which pathogens are responsible for infection, which antimi-
PSB specimens. Other authors have emphasized that, although quan- crobial agents to use, and whether to continue therapy (Fig. 59-2).
titative endotracheal aspirate cultures can correctly identify patients One major technical problem with all bronchoscopic techniques
with pneumonia, microbiologic results cannot be used to infer which is proper selection of the sampling area in the tracheobronchial tree.
microorganisms present in the trachea are really present in the lungs. In Almost all intubated patients have purulent-looking secretions and
a study comparing quantitative endotracheal aspirate culture results to the secretions first seen may represent those aspirated from another
postmortem quantitative lung-biopsy cultures, only 53% of the microor- site into gravity-dependent airways or from upper-airway secretions
ganisms isolated from the former samples at concentrations >10 cfu/mL aspirated around the endotracheal tube. Usually, the sampling area is
7
were also found in the latter cultures. 188 selected based on the location of infiltrate on chest radiograph or the
The inherent advantage of quantitative cultures of endotracheal aspi- segment visualized during bronchoscopy as having purulent secre-
rates is that they are more specific, permitting the discontinuation of tions. Collection of secretions in the lower trachea or mainstem
193
section04.indd 526 1/23/2015 2:20:34 PM