Page 708 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 708
CHAPTER 59: Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia 527
No further No
investigation; Clinical features
suggesting VAP
observe
Yes
Immediate sampling of distal airways
by BAL/PSB before changing existing antibiotics
Direct specimen
examination
Observe, No Positive Observe; No Signs of No
look for another quantitati look for another severe Bacteria
infection(s) vecultures infection(s) sepsis present
Yes
Yes
Yes
Start antibiotics
Start antibiotics immediately using
Start antibiotics immediately using direct specimen
based on ATS guidelines examination results
culture results and local epidemiology
Continue or adjust No Positive Positive No Continue or adjust
antibiotics; look for quantitati quantitati antibiotics; look for
another infection(s) vecultures vecultures another infection(s)
Yes Yes
Adjust antibiotics Adjust antibiotics
based on culture results based on culture results
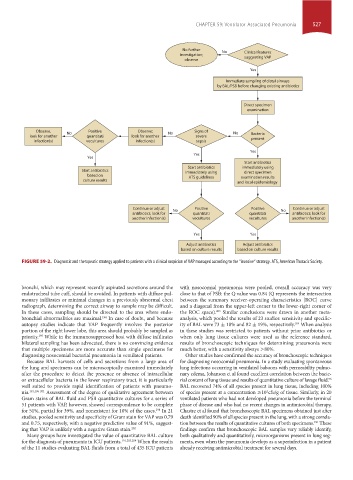
FIGURE 59-2. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategy applied to patients with a clinical suspicion of VAP managed according to the “invasive” strategy. ATS, American Thoracic Society.
bronchi, which may represent recently aspirated secretions around the with nosocomial pneumonia were pooled, overall accuracy was very
endotracheal tube cuff, should be avoided. In patients with diffuse pul- close to that of PSB: the Q value was 0.84 (Q represents the intersection
monary infiltrates or minimal changes in a previously abnormal chest between the summary receiver-operating characteristics [ROC] curve
radiograph, determining the correct airway to sample may be difficult. and a diagonal from the upper-left corner to the lower-right corner of
In these cases, sampling should be directed to the area where endo- the ROC space). Similar conclusions were drawn in another meta-
203
bronchial abnormalities are maximal. In case of doubt, and because analysis, which pooled the results of 23 studies: sensitivity and specific-
194
autopsy studies indicate that VAP frequently involves the posterior ity of BAL were 73 ± 18% and 82 ± 19%, respectively. When analysis
204
portion of the right lower lobe, this area should probably be sampled as in these studies was restricted to patients without prior antibiotics or
priority. While in the immunosuppressed host with diffuse infiltrates when only lung tissue cultures were used as the reference standard,
195
bilateral sampling has been advocated, there is no convincing evidence results of bronchoscopic techniques for determining pneumonia were
that multiple specimens are more accurate than single specimens for much better, with a sensitivity always >80%.
diagnosing nosocomial bacterial pneumonia in ventilated patients. Other studies have confirmed the accuracy of bronchoscopic techniques
Because BAL harvests of cells and secretions from a large area of for diagnosing nosocomial pneumonia. In a study evaluating spontaneous
the lung and specimens can be microscopically examined immediately lung infections occurring in ventilated baboons with permeability pulmo-
after the procedure to detect the presence or absence of intracellular nary edema, Johanson et al found excellent correlation between the bacte-
or extracellular bacteria in the lower respiratory tract, it is particularly rial content of lung tissue and results of quantitative culture of lavage fluid.
96
well suited to provide rapid identification of patients with pneumo- BAL recovered 74% of all species present in lung tissue, including 100%
nia. 191,196-201 Assessment of the degree of qualitative agreement between of species present at a concentration ≥10 cfu/g of tissue. Similarly, in 20
4
Gram stains of BAL fluid and PSB quantitative cultures for a series of ventilated patients who had not developed pneumonia before the terminal
51 patients with VAP, however, showed correspondence to be complete phase of disease and who had no recent changes in antimicrobial therapy,
for 51%, partial for 39%, and nonexistent for 10% of the cases. In 21 Chastre et al found that bronchoscopic BAL specimens obtained just after
198
studies, pooled sensitivity and specificity of Gram stain for VAP was 0.79 death identified 90% of all species present in the lung, with a strong correla-
and 0.75, respectively, with a negative predictive value of 91%, suggest- tion between the results of quantitative cultures of both specimens. These
191
ing that VAP is unlikely with a negative Gram stain. 202 findings confirm that bronchoscopic BAL samples very reliably identify,
Many groups have investigated the value of quantitative BAL culture both qualitatively and quantitatively, microorganisms present in lung seg-
for the diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU patients. 191,203,204 When the results ments, even when the pneumonia develops as a superinfection in a patient
of the 11 studies evaluating BAL fluids from a total of 435 ICU patients already receiving antimicrobial treatment for several days.
section04.indd 527 1/23/2015 2:20:35 PM