Page 251 - Psychology of Wounds and Wound Care in Clinical Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 251
226 Chapter 9. Conclusion
Positive factors Negative factors
Psychosocial
Social support
factors
Psychological
resources Pain Social environment
Positive
therapeutic Stress
relationship
Patient Well-Being
Wound type
Wound treatment
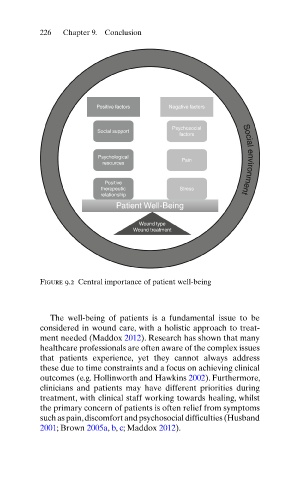
Figure 9.2 Central importance of patient well-being
The well-being of patients is a fundamental issue to be
considered in wound care, with a holistic approach to treat-
ment needed (Maddox 2012 ). Research has shown that many
healthcare professionals are often aware of the complex issues
that patients experience, yet they cannot always address
these due to time constraints and a focus on achieving clinical
outcomes (e.g. Hollinworth and Hawkins 2002 ). Furthermore,
clinicians and patients may have different priorities during
treatment, with clinical staff working towards healing, whilst
the primary concern of patients is often relief from symptoms
such as pain, discomfort and psychosocial difficulties (Husband
;
2001 Brown 2005a , b , c Maddox 2012 ).
;