Page 335 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 335
ECA5 7/18/06 6:51 PM Page 320
320 The head and neck
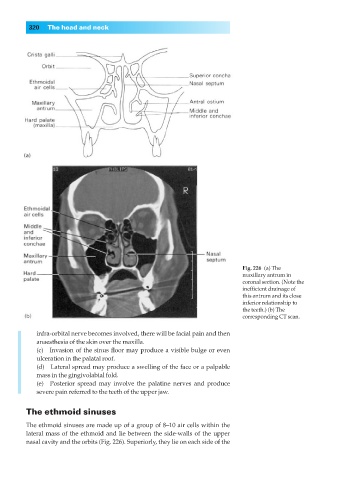
Fig. 226◊(a) The
maxillary antrum in
coronal section. (Note the
inefficient drainage of
this antrum and its close
inferior relationship to
the teeth.) (b) The
corresponding CT scan.
infra-orbital nerve becomes involved, there will be facial pain and then
anaesthesia of the skin over the maxilla.
(c) Invasion of the sinus floor may produce a visible bulge or even
ulceration in the palatal roof.
(d) Lateral spread may produce a swelling of the face or a palpable
mass in the gingivolabial fold.
(e) Posterior spread may involve the palatine nerves and produce
severe pain referred to the teeth of the upper jaw.
The ethmoid sinuses
The ethmoid sinuses are made up of a group of 8–10 air cells within the
lateral mass of the ethmoid and lie between the side-walls of the upper
nasal cavity and the orbits (Fig. 226). Superiorly, they lie on each side of the