Page 162 - Critical Care Notes
P. 162
4223_Tab05_141-174 29/08/14 8:28 AM Page 156
NEURO
■ In CVA, disruption of blood flow to the brain →↓ O 2 and glucose to the
brain → ischemic cascade → neurons unable to maintain aerobic respira-
tion → switch to anaerobic respiration → build-up of lactic acid → change in
blood pH → influx of intracellular calcium and increase in glutamate →
destroys cell membrane → cell membrane and proteins break down,
forming free radicals → cell injury and death → neurological dysfunction.
■ Low cerebral blood flow →↓ O 2 to the brain →↑ extraction of O 2 by
the brain.
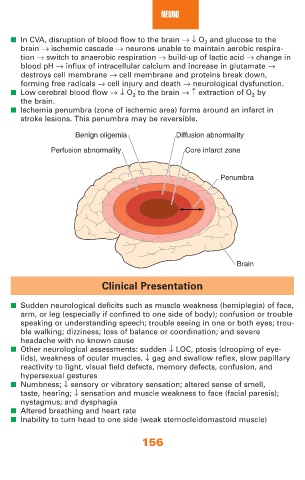
■ Ischemia penumbra (zone of ischemic area) forms around an infarct in
stroke lesions. This penumbra may be reversible.
Benign oligemia Diffusion abnormality
Perfusion abnormality Core infarct zone
Penumbra
Brain
Clinical Presentation
■ Sudden neurological deficits such as muscle weakness (hemiplegia) of face,
arm, or leg (especially if confined to one side of body); confusion or trouble
speaking or understanding speech; trouble seeing in one or both eyes; trou-
ble walking; dizziness; loss of balance or coordination; and severe
headache with no known cause
■ Other neurological assessments: sudden ↓ LOC, ptosis (drooping of eye-
lids), weakness of ocular muscles, ↓ gag and swallow reflex, slow papillary
reactivity to light, visual field defects, memory defects, confusion, and
hypersexual gestures
■ Numbness; ↓ sensory or vibratory sensation; altered sense of smell,
taste, hearing; ↓ sensation and muscle weakness to face (facial paresis);
nystagmus; and dysphagia
■ Altered breathing and heart rate
■ Inability to turn head to one side (weak sternocleidomastoid muscle)
156