Page 27 - Critical Care Notes
P. 27
4223_Tab01_001-044 29/08/14 10:46 AM Page 21
21
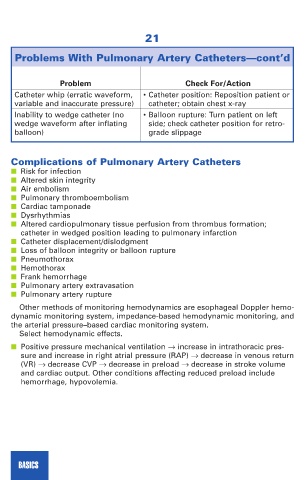
Problems With Pulmonary Artery Catheters—cont’d
Problem Check For/Action
Catheter whip (erratic waveform, • Catheter position: Reposition patient or
variable and inaccurate pressure) catheter; obtain chest x-ray
Inability to wedge catheter (no • Balloon rupture: Turn patient on left
wedge waveform after inflating side; check catheter position for retro-
balloon) grade slippage
Complications of Pulmonary Artery Catheters
■ Risk for infection
■ Altered skin integrity
■ Air embolism
■ Pulmonary thromboembolism
■ Cardiac tamponade
■ Dysrhythmias
■ Altered cardiopulmonary tissue perfusion from thrombus formation;
catheter in wedged position leading to pulmonary infarction
■ Catheter displacement/dislodgment
■ Loss of balloon integrity or balloon rupture
■ Pneumothorax
■ Hemothorax
■ Frank hemorrhage
■ Pulmonary artery extravasation
■ Pulmonary artery rupture
Other methods of monitoring hemodynamics are esophageal Doppler hemo-
dynamic monitoring system, impedance-based hemodynamic monitoring, and
the arterial pressure–based cardiac monitoring system.
Select hemodynamic effects.
■ Positive pressure mechanical ventilation → increase in intrathoracic pres-
sure and increase in right atrial pressure (RAP) → decrease in venous return
(VR) → decrease CVP → decrease in preload → decrease in stroke volume
and cardiac output. Other conditions affecting reduced preload include
hemorrhage, hypovolemia.
BASICS