Page 176 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 176
142 Chapter 5
and bronchocutaneous fistulas, DLTs can provide ventilation by overcoming the
persistent air leak through the fistulas (Barash, 2001).
Selection of DLT
It is essential to use the largest DLT appropriate for the patient since most
It is essential to use the complications associated with DLTs result from using small tubes. Recogniz-
largest DLT appropriate for the
patient. ing the diameter of the bronchus (usually the left) is a crucial determinant of
success in the use of a DLT. On a typical posterior-anterior (PA) chest radiog-
raphy, the air bronchogram is enlarged by 10% as the bronchi are about 15 cm
from the plate (Russell, 2004). If the bronchi are not visible on the chest radi-
ography, the diameter of the left bronchus may be estimated by using 68% of
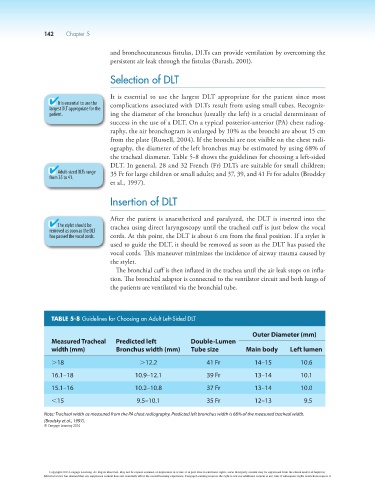
the tracheal diameter. Table 5-8 shows the guidelines for choosing a left-sided
DLT. In general, 28 and 32 French (Fr) DLTs are suitable for small children;
Adult-sized DLTs range 35 Fr for large children or small adults; and 37, 39, and 41 Fr for adults (Brodsky
from 35 to 41.
et al., 1997).
Insertion of DLT
After the patient is anaesthetized and paralyzed, the DLT is inserted into the
The stylet should be trachea using direct laryngoscopy until the tracheal cuff is just below the vocal
removed as soon as the DLT
has passed the vocal cords. cords. At this point, the DLT is about 6 cm from the final position. If a stylet is
used to guide the DLT, it should be removed as soon as the DLT has passed the
vocal cords. This maneuver minimizes the incidence of airway trauma caused by
the stylet.
The bronchial cuff is then inflated in the trachea until the air leak stops on infla-
tion. The bronchial adaptor is connected to the ventilator circuit and both lungs of
the patients are ventilated via the bronchial tube.
TABLE 5-8 Guidelines for Choosing an Adult Left-Sided DLT
Outer Diameter (mm)
Measured tracheal Predicted left Double-Lumen
width (mm) bronchus width (mm) tube size Main body Left lumen
.18 .12.2 41 Fr 14–15 10.6
16.1–18 10.9–12.1 39 Fr 13–14 10.1
15.1–16 10.2–10.8 37 Fr 13–14 10.0
,15 9.5–10.1 35 Fr 12–13 9.5
Note: Tracheal width as measured from the PA chest radiography. Predicted left bronchus width is 68% of the measured tracheal width.
(Brodsky et al., 1997).
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.