Page 268 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 268
234 Chapter 8
SUMMARY
Initiation of mechanical ventilation requires many decisions, ranging from the mode of
ventilation to the level of PEEP. Nevertheless, this process can be simplified by follow-
ing a set of established guidelines. Under most clinical conditions, the initial settings
on the ventilator will satisfy the immediate requirement for most patients.
It is essential to remember that the initial settings are just that; subsequent changes
to these settings must be made based on the ever-changing condition of the pa-
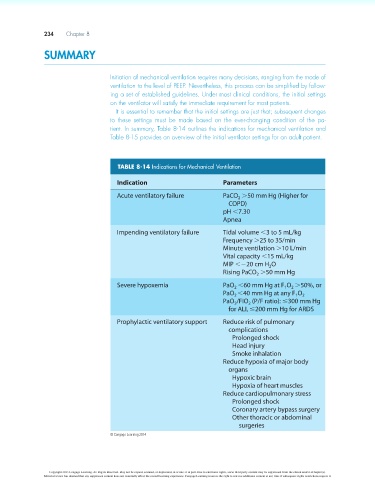
tient. In summary, Table 8-14 outlines the indications for mechanical ventilation and
Table 8-15 provides an overview of the initial ventilator settings for an adult patient.
TABLE 8-14 Indications for Mechanical Ventilation
Indication Parameters
Acute ventilatory failure PaCO .50 mm Hg (Higher for
2
COPD)
pH ,7.30
Apnea
Impending ventilatory failure Tidal volume ,3 to 5 mL/kg
Frequency .25 to 35/min
Minute ventilation .10 L/min
Vital capacity ,15 mL/kg
MIP ,220 cm H O
2
Rising PaCO .50 mm Hg
2
Severe hypoxemia PaO ,60 mm Hg at F O .50%, or
2
2
1
PaO ,40 mm Hg at any F O 2
2
1
PaO /FIO (P/F ratio): ≤300 mm Hg
2
2
for ALI, ≤200 mm Hg for ARDS
Prophylactic ventilatory support Reduce risk of pulmonary
complications
Prolonged shock
Head injury
Smoke inhalation
Reduce hypoxia of major body
organs
Hypoxic brain
Hypoxia of heart muscles
Reduce cardiopulmonary stress
Prolonged shock
Coronary artery bypass surgery
Other thoracic or abdominal
surgeries
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.