Page 269 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 269
Initiation of Mechanical Ventilation 235
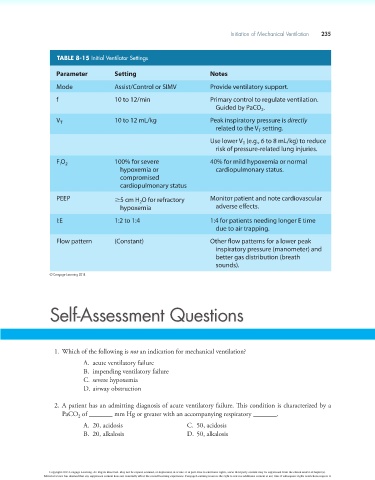
TABLE 8-15 Initial Ventilator Settings
Parameter Setting Notes
Mode Assist/Control or SIMV Provide ventilatory support.
f 10 to 12/min Primary control to regulate ventilation.
Guided by PaCO .
2
V T 10 to 12 mL/kg Peak inspiratory pressure is directly
related to the V setting.
T
Use lower V (e.g., 6 to 8 mL/kg) to reduce
T
risk of pressure-related lung injuries.
F O 2 100% for severe 40% for mild hypoxemia or normal
I
hypoxemia or cardiopulmonary status.
compromised
cardiopulmonary status
PEEP ≥5 cm H O for refractory Monitor patient and note cardiovascular
2
hypoxemia adverse effects.
I:E 1:2 to 1:4 1:4 for patients needing longer E time
due to air trapping.
Flow pattern (Constant) Other flow patterns for a lower peak
inspiratory pressure (manometer) and
better gas distribution (breath
sounds).
© Cengage Learning 2014
Self-Assessment Questions
1. Which of the following is not an indication for mechanical ventilation?
A. acute ventilatory failure
B. impending ventilatory failure
C. severe hypoxemia
D. airway obstruction
2. A patient has an admitting diagnosis of acute ventilatory failure. This condition is characterized by a
PaCO of _______ mm Hg or greater with an accompanying respiratory _______.
2
A. 20, acidosis C. 50, acidosis
B. 20, alkalosis D. 50, alkalosis
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.