Page 619 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 619
Mechanical Ventilation in Nontraditional Settings 585
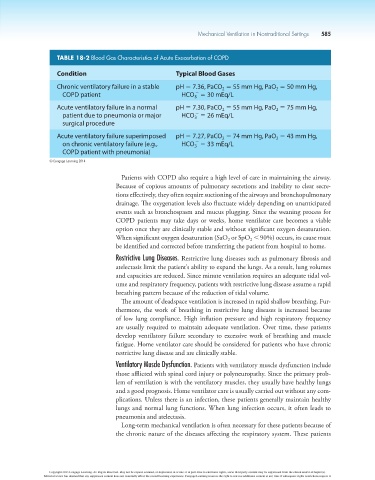
TABLE 18-2 Blood Gas Characteristics of Acute Exacerbation of COPD
Condition Typical Blood Gases
Chronic ventilatory failure in a stable pH 5 7.36, PaCO 5 55 mm Hg, PaO 5 50 mm Hg,
2
2
-
COPD patient HCO 5 30 mEq/L
3
Acute ventilatory failure in a normal pH 5 7.30, PaCO 5 55 mm Hg, PaO 5 75 mm Hg,
2
2
-
patient due to pneumonia or major HCO 5 26 mEq/L
3
surgical procedure
Acute ventilatory failure superimposed pH 5 7.27, PaCO 5 74 mm Hg, PaO 5 43 mm Hg,
2
2
-
on chronic ventilatory failure (e.g., HCO 5 33 mEq/L
3
COPD patient with pneumonia)
© Cengage Learning 2014
Patients with COPD also require a high level of care in maintaining the airway.
Because of copious amounts of pulmonary secretions and inability to clear secre-
tions effectively, they often require suctioning of the airways and bronchopulmonary
drainage. The oxygenation levels also fluctuate widely depending on unanticipated
events such as bronchospasm and mucus plugging. Since the weaning process for
COPD patients may take days or weeks, home ventilator care becomes a viable
option once they are clinically stable and without significant oxygen desaturation.
When significant oxygen desaturation (SaO or SpO , 90%) occurs, its cause must
2
2
be identified and corrected before transferring the patient from hospital to home.
Restrictive Lung Diseases. Restrictive lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis and
atelectasis limit the patient’s ability to expand the lungs. As a result, lung volumes
and capacities are reduced. Since minute ventilation requires an adequate tidal vol-
ume and respiratory frequency, patients with restrictive lung disease assume a rapid
breathing pattern because of the reduction of tidal volume.
The amount of deadspace ventilation is increased in rapid shallow breathing. Fur-
thermore, the work of breathing in restrictive lung diseases is increased because
of low lung compliance. High inflation pressure and high respiratory frequency
are usually required to maintain adequate ventilation. Over time, these patients
develop ventilatory failure secondary to excessive work of breathing and muscle
fatigue. Home ventilator care should be considered for patients who have chronic
restrictive lung disease and are clinically stable.
Ventilatory Muscle Dysfunction. Patients with ventilatory muscle dysfunction include
those afflicted with spinal cord injury or polyneuropathy. Since the primary prob-
lem of ventilation is with the ventilatory muscles, they usually have healthy lungs
and a good prognosis. Home ventilator care is usually carried out without any com-
plications. Unless there is an infection, these patients generally maintain healthy
lungs and normal lung functions. When lung infection occurs, it often leads to
pneumonia and atelectasis.
Long-term mechanical ventilation is often necessary for these patients because of
the chronic nature of the diseases affecting the respiratory system. These patients
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.