Page 174 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 174
50
50
ara
P
p13
g
P
52.
9/2
52.
qxd
Apt
e 1
0
009
06_
LWBK340-c06_06_p132-152.qxd 09/09/2009 08:25 AM Page 150 Aptara
L L LWB
K34
K34
0-c
5 A
M
8:2
LWB K34 0-c 06_ p13 2-1 52. qxd 0 9/0 9/2 009 0 0 8:2 5 A M P a a g e 1 50 Apt ara
2-1
9/0
150 PA R T I I / Physiologic and Pathologic Responses
31
vein occurs and can lead to adrenal hemorrhage. Arterial throm-
botic complications include limb artery thrombosis, thrombotic
stroke, myocardial infarction, or other arterial thrombosis (mesen-
31
tery or spinal). Skin necrosis at heparin injection sites is another
presentation that can range from painful erythematous papules to
p
p
pa
p
pa
p
pa
m
m
m
m
m
a
a
m
m
m
m
m
m
m
mu
p
un
n
n
u
u
u
n
ne
n
n
n
n
n
u
e
e
e
p
e
e
ep
u
u
u
Heparin
H H H H H H H H H H H He
u
i
i
r
m
m
m
m
r
a
a
r
ri
I I I I Immunee e e e e e e e e He e e ep ar ri in n n n n n n n n dermal necrosis. Warfarin necrosis with HIT is characterized by
m
m
m
a
a
mm
m
m
m
m
m
a
ar
m
m
m
e
e
e
l
l
e
e
e
e
e
p
p
p
c c c c c c c c complexxex x x x x x x x
p
p
l
p
p
p
m
o
o
o
m
o
o
o
o
m
m
m
m
o
m
m
m
o
m
m
4
PF44
PF
4
F
P P P P P P P P P P F 4 venous limb gangrene usually with DVT or classic necrosis in
4
F
F
4
4
F4
4
F4
F
F
F
4
F4
nonacral sites (breasts, abdominal wall, thigh, calf, or forearm).
Overt DIC is another sequelae of HIT that occurs in 10% to 20%
Fc
Fc
Fc
Fc
Fc
Fc
c re
ep
c r
c r
c r
or
F F F F F F F Fc
Fc
ep
Fc receptor r r r
Fc
Fc
ep
o
or
or
or
or
o
ep
re
re
re
pt
re
rec
pto
pt
pto
re
re
ec
ec
ec
ce
ec
ec
ce
pto
ce
ece
ec
p
or
ce
to
to
ep
ep
ce
ep
pt
pt
c re
c r
ce
to
to
ce
of patients. There has even been anaphylactic reaction to IV he-
et
et
et
et
et
et
et
Pla at te le et t t t
Pla
ate
at
ate
ate
at
Platelet
Pla
Pl Pl Pl P P P P P P P P
la
la
la
a
ele
ele
ele
ele
el
le
le
e
el
te
at
te
te
parin 5 to 30 minutes after administration with symptoms rang-
ing from cardiac arrest to an inflammatory presentation, that is,
fever, chills, rigors, or flushing. 31
Arterial thrombosis usually involves the distal portion of the
va
v
ov
ov
v
v
a
a
a
a
a
va
va
a
a
a
remo
rem
rem
ate
ate
rem
rem
elet
emo
emo
ate
let
let
tel
tele
elet
t re
t re
ate
et re
et r
atel
ate
et re
et re
et r
Platelet removallal
Pla
Plat
mo
mo
Pl Pl P P P P P P
ele
ele
ele
Pla
Pla tele t rem ov v v v v v va l l l l l l l l l l Platelet a activ v v v v a atio n n n n aorta, and the symptoms can vary in degree depending on the
elet
lat
Pla
Pla
emo
emo
lat
mo
mo
mo
mo
Pla
mo
at
ati
ati
atio
a
iv
t acti
atio
activ
iv
atio
ctiv
a
ctiv
tiv
ctiv
a
activ
activ
activ
a
atio
at
tion
tion
Platelet activationation
tion
atelet ac
atelet a
P Pl Pl Plate
Platelet
Platel
Platele
Platelet a
Plate
Platele
Platelet
Platelet
ion
et act
et acti
on
on
on
on
on
t
elet ac
let act
elet ac
y sp
y sp
y spl
y sple
by
by
by
by
by
by
by
by
b b by
by splenicic
by
by
b b y spl lenic thrombus size. Absent pulses indicate total arterial thrombosis oc-
plenic
splen
plenic
plenic
plenic
sple
sple
splen
sple
splen
nic
enic
nic
ic
nic
enic
pleni
enic
enic
enic
s
s
y
s
sp
s
y
sp
croph
croph
croph
crop
macrop phage es
crophages
crop
ages
es
ges
ges
ages
ges
ages
ges
hages
ophag
ophag
acrop
opha
ropha
ropha
ophag
ropha
phage
phage
hages
hages
hages
phages
clusion whereas pulses with distal extremity ischemia indicate mi-
31
crovascular occlusion. The classic presentation for acute arterial
Platelet release thrombosis is known as the “6 Ps”: pallor, pulselessness, pain,
paresthesias, paralysis, and poikilothermy (coolness). 24 Either the
Release of
Thrombocytopenia procoagulant arms or the legs can be involved. The pain and paralysis are the re-
microparticles sult of nerve and skeletal muscle ischemia that can occur as early
Platelet as 4 to 6 hours after the occlusion. Beyond this time period, the
aggregation situation can progress to potential compartment syndrome with
severe pain, tense swelling, and muscle tenderness of the affected
extremity. 24 In HIT, limb amputation is common.
Thrombosis Medical Management
Medical management is challenged with making the diagnosis of
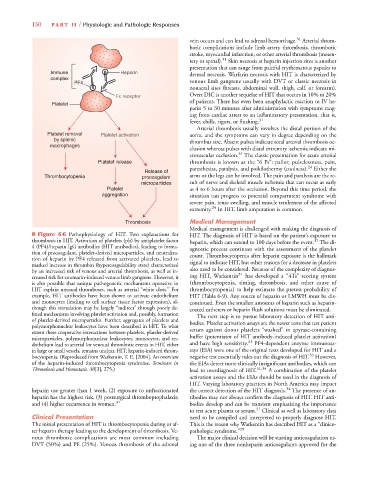
■ Figure 6-6 Pathophysiology of HIT. Two explanations for HIT. The diagnosis of HIT is based on the patient’s exposure to
thrombosis in HIT. Activation of platelets (plt) by antiplatelet factor heparin, which can extend to 100 days before the event. The di-
32
4 (PF4)/heparin IgG antibodies (HIT antibodies), leading to forma- agnostic process continues with the assessment of the platelet
tion of procoagulant, platelet-derived microparticles, and neutraliza- count. Thrombocytopenia after heparin exposure is the hallmark
tion of heparin by PF4 released from activated platelets, lead to
marked increase in thrombin (hypercoagulability state) characterized signal to indicate HIT, but other reasons for a decrease in platelets
by an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis, as well as in- also need to be considered. Because of the complexity of diagnos-
31
creased risk for coumarin-induced venous limb gangrene. However, it ing HIT, Warkentin has developed a “4Ts” scoring system
is also possible that unique pathogenetic mechanisms operative in (thrombocytopenia, timing, thrombosis, and other cause of
HIT explain unusual thromboses, such as arterial “white clots.’’ For thrombocytopenia) to help estimate the pretest probability of
example, HIT antibodies have been shown to activate endothelium HIT (Table 6-9). Any source of heparin or LMWH must be dis-
and monocytes (leading to cell surface tissue factor expression), al- continued. Even the smallest amounts of heparin such as heparin-
though this stimulation may be largely “indirect’’ through poorly de- coated catheters or heparin flush solutions must be eliminated.
fined mechanisms involving platelet activation and, possibly, formation The next step is to pursue laboratory detection of HIT anti-
of platelet-derived microparticles. Further, aggregates of platelets and bodies. Platelet activation assays are the newer tests that test patient
polymorphonuclear leukocytes have been described in HIT. To what
extent these cooperative interactions between platelets, platelet-derived serum against donor platelets “washed” in apyrase-containing
microparticles, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and en- buffer (potentiator of HIT antibody-induced platelet activation)
31
dothelium lead to arterial (or venous) thrombotic events in HIT, either and have high sensitivity. PF4-dependent enzyme immunoas-
in large or small vessels, remains unclear. HIT, heparin-induced throm- says (EIA) were one of the original tests developed for HIT and a
33
bocytopenia. (Reproduced from Warkentin, T. E. [2004]. An overview negative test essentially rules out the diagnosis of HIT. However,
of the heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome. Seminars in the EIAs detect more clinically insignificant antibodies, which can
Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 30[3], 275.) lead to overdiagnosis of HIT. 31,34 A combination of the platelet
activation assays and the EIAs should be used in the diagnosis of
HIT. Varying laboratory practices in North America may impact
34
heparin use greater than 1 week, (2) exposure to unfractionated the correct detection of the HIT diagnosis. The presence of an-
heparin has the highest risk, (3) postsurgical thromboprophalaxis; tibodies may not always confirm the diagnosis of HIT. HIT anti-
and (4) higher occurrence in women. 31 bodies develop and can be transient emphasizing the importance
to test acute plasma or serum. 31 Clinical as well as laboratory data
Clinical Presentation need to be compiled and interpreted to properly diagnose HIT.
The initial presentation of HIT is thrombocytopenia during or af- This is the reason why Warkentin has described HIT as a “clinico-
ter heparin therapy leading to the development of thrombosis. Ve- pathologic syndrome.” 29
nous thrombotic complications are most common including The major clinical decision will be starting anticoagulation us-
DVT (50%) and PE (25%). Venous thrombosis of the adrenal ing one of the three nonheparin anticoagulants approved for the