Page 274 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 274
1
1
1
/09
/09
/09
0:2
M
M
Pa
0:2
1 P
1 P
66.
q
q
5-2
5-2
66.
q
6
/29
/29
xd
xd
6
ara
ara
a
p
t
t
a
In
c.
c.
a
a
In
g
g
e 2
Pa
Pa
g
e 2
A
p
p
50
50
A
0-c
LWB K34 0-c 11_ p p pp245-266.qxd 6/29/09 10:21 PM Page 250 Aptara Inc.
24
24
LWBK340-c11_
K34
11_
LWB
250 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
troponin to leak into the bloodstream in patients with no evidence
of coronary artery disease. Patients with critical illness and tro-
5X ponin elevations have been found to have a worse prognosis. 21,31
See Display 11-1 for elevations of troponin in the absence of overt
ischemic heart disease.
4X
Enzyme levels Increase above normal 3X diseases. This elevation is usually associated with right heart
Troponin elevation may be seen in patients with pulmonary
strain. Of patients diagnosed with moderate-to-large pulmonary
embolism (PE), 30–50% have elevated troponin levels. This ele-
2X
ropon
T
Normal range AS Troponin vation may be from the acute right heart overload and has been
21,31
associated with significant increase in mortality.
Assessing for myocardial damage after blunt cardiac trauma
AST
D
LDH
C
CK
may be difficult given the high rate of false-positive and false-
negative results when using CK-MB. Troponin-I along with ECG
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
has emerged as an accurate test for confirming presence of my-
Chest pain Days after infarction
ocardial damage after cardiac contusion. 24,32
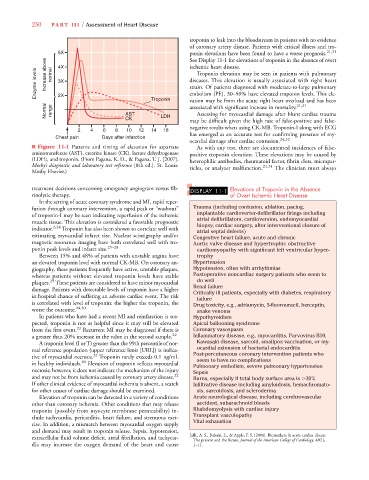
■ Figure 11-1 Patterns and timing of elevation for aspartate As with any test, there are documented incidences of false-
aminotransferase (AST), creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase positive troponin elevation. These elevations may be caused by
(LDH), and troponin. (From Pagana, K. D., & Pagana, T. J. [2007]. heterophilic antibodies, rheumatoid factor, fibrin clots, micropar-
Mosby’s diagnostic and laboratory test reference [8th ed.]. St. Louis: ticles, or analyzer malfunction. 21,31 The clinician must always
Mosby Elsevier.)
treatment decisions concerning emergency angiogram versus fib- DISPLAY 11-1 Elevations of Troponin in the Absence
rinolytic therapy. of Overt Ischemic Heart Disease
In the setting of acute coronary syndrome and MI, rapid reper-
fusion through coronary intervention, a rapid peak or “washout” Trauma (including contusion, ablation, pacing,
of troponin-I may be seen indicating reperfusion of the ischemic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator firings including
muscle tissue. This elevation is considered a favorable prognostic atrial defibrillators, cardioversion, endomyocardial
biopsy, cardiac surgery, after interventional closure of
indicator. 2,24 Troponin has also been shown to correlate well with atrial septal defects)
estimating myocardial infarct size. Nuclear scintigraphy and/or Congestive heart failure, acute and chronic
magnetic resonance imaging have both correlated well with tro- Aortic valve disease and hypertrophic obstructive
ponin peak levels and infarct size. 25–28 cardiomyopathy with significant left ventricular hyper-
Between 15% and 48% of patients with unstable angina have trophy
an elevated troponin level with normal CK-MB. On coronary an- Hypertension
giography, these patients frequently have active, unstable plaques, Hypotension, often with arrhythmias
whereas patients without elevated troponin levels have stable Postoperative noncardiac surgery patients who seem to
29
plaques. These patients are considered to have minor myocardial do well
damage. Patients with detectable levels of troponin have a higher Renal failure
Critically ill patients, especially with diabetes, respiratory
in hospital chance of suffering an adverse cardiac event. The risk failure
is correlated with level of troponin: the higher the troponin, the Drug toxicity, e.g., adriamycin, 5-fluorouracil, herceptin,
worse the outcome. 24,30 snake venoms
In patients who have had a recent MI and reinfarction is sus- Hypothyroidism
pected, troponin is not as helpful since it may still be elevated Apical ballooning syndrome
from the first event. 23 Recurrent MI may be diagnosed if there is Coronary vasospasm
a greater than 20% increase in the value in the second sample. 22 Inflammatory disease, e.g., myocarditis, Parvovirus B10,
A troponin level (I or T) greater than the 99th percentile of nor- Kawasaki disease, sarcoid, smallpox vaccination, or my-
mal reference population (upper reference limit [URL]) is indica- ocardial extension of bacterial endocarditis
tive of myocardial necrosis. 22 Troponin rarely exceeds 0.1 ng/mL Post-percutaneous coronary intervention patients who
seem to have no complications
in healthy individuals. 20 Elevation of troponin reflects myocardial Pulmonary embolism, severe pulmonary hypertension
necrosis; however, it does not indicate the mechanism of the injury Sepsis
and may not be from ischemia caused by coronary artery disease. 22 Burns, especially if total body surface area is 30%
If other clinical evidence of myocardial ischemia is absent, a search Infiltrative disease including amyloidosis, hemachromato-
for other causes of cardiac damage should be examined. sis, sarcoidosis, and scleroderma
Elevation of troponin can be detected in a variety of conditions Acute neurological disease, including cerebrovascular
other than coronary ischemia. Other conditions that may release accident, subarachnoid bleeds
troponin (possibly from myocyte membrane permeability) in- Rhabdomyolysis with cardiac injury
clude tachycardia, pericarditis, heart failure, and strenuous exer- Transplant vasculopathy
cise. In addition, a mismatch between myocardial oxygen supply Vital exhaustion
and demand may result in troponin release. Sepsis, hypotension,
Jaffe, A. S., Babuin, L., & Apple, F. S. [2006]. Biomarkers in acute cardiac disease—
extracellular fluid volume deficit, atrial fibrillation, and tachycar-
The present and the future. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 48(1),
dia may increase the oxygen demand of the heart and cause 1–11.