Page 905 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 905
6-8
6-8
009
009
qx
qx
88.
88.
1
1
0:0
0:0
p87
p87
1
009
d
0
2
2
0
/
/
6
6
2
9
d
2
/
/
9
9
a
a
39_
ar
Apt
Apt
ar
39_
LWB
L L LWB
LWBK340-c39_39_p87p876-888.qxd 29/06/2009 10:01 PM Page 881 Aptara
K34
0-c
0-c
K34
g
g
1 P
Pa
M
M
Pa
1 P
81
81
Apt
0:0
e 8
e 8
C HAPTER 39 / Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome 881
Factors Contributing to Cardiometabolic Risk
Abnormal Lipid
Overweight/Obesity Metabolism
• LDL
Genetics Age
• ApoB
• HDL
Insulin Resistance
nsulin Resistance
? • Triglycerides
Insulin Resistance Syndrome
Cardiometabolic
Lipids BP Glucose
Risk
Global Diabetes CVD Risk
Age, Race, Sex,
Family History
Smoking,
Physical inactivity,
Unhealthy Eating Inflammation,
Hypercoagulation
Hypertension
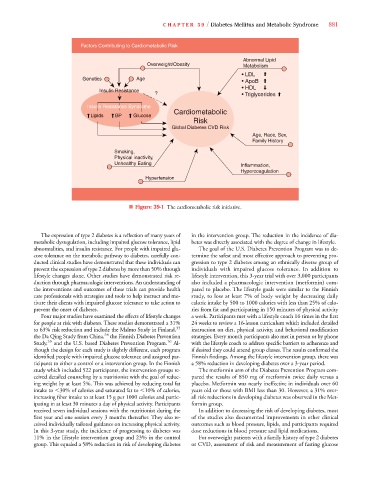
■ Figure 39-1 The cardiometabolic risk initiative.
The expression of type 2 diabetes is a reflection of many years of in the intervention group. The reduction in the incidence of dia-
metabolic dysregulation, including impaired glucose tolerance, lipid betes was directly associated with the degree of change in lifestyle.
abnormalities, and insulin resistance. For people with impaired glu- The goal of the U.S. Diabetes Prevention Program was to de-
cose tolerance on the metabolic pathway to diabetes, carefully con- termine the safest and most effective approach to preventing pro-
ducted clinical studies have demonstrated that these individuals can gression to type 2 diabetes among an ethnically diverse group of
prevent the expression of type 2 diabetes by more than 50% through individuals with impaired glucose tolerance. In addition to
lifestyle changes alone. Other studies have demonstrated risk re- lifestyle intervention, this 3-year trial with over 3,000 participants
duction through pharmacologic interventions. An understanding of also included a pharmacologic intervention (metformin) com-
the interventions and outcomes of these trials can provide health pared to placebo. The lifestyle goals were similar to the Finnish
care professionals with strategies and tools to help instruct and mo- study, to lose at least 7% of body weight by decreasing daily
tivate their clients with impaired glucose tolerance to take action to caloric intake by 500 to 1000 calories with less than 25% of calo-
prevent the onset of diabetes. ries from fat and participating in 150 minutes of physical activity
Four major studies have examined the effects of lifestyle changes a week. Participants met with a lifestyle coach 16 times in the first
for people at risk with diabetes. These studies demonstrated a 31% 24 weeks to review a 16-lesson curriculum which included detailed
to 63% risk reduction and include the Malmo Study in Finland, 33 instruction on diet, physical activity, and behavioral modification
34
the Da Qing Study from China, the Finnish Diabetes Prevention strategies. Every month participants also met in person or by phone
Study, 35 and the U.S. based Diabetes Prevention Program. 16 Al- with the lifestyle coach to address specific barriers to adherence and
though the design for each study is slightly different, each program if desired they could attend group classes. The results confirmed the
identified people with impaired glucose tolerance and assigned par- Finnish findings. Among the lifestyle intervention group, there was
ticipants to either a control or a intervention group. In the Finnish a 58% reduction in developing diabetes over a 3-year period.
study which included 522 participants, the intervention groups re- The metformin arm of the Diabetes Prevention Program com-
ceived detailed counseling by a nutritionist with the goal of reduc- pared the results of 850 mg of metformin twice daily versus a
ing weight by at least 5%. This was achieved by reducing total fat placebo. Metformin was nearly ineffective in individuals over 60
intake to 30% of calories and saturated fat to 10% of calories, years old or those with BMI less than 30. However, a 31% over-
increasing fiber intake to at least 15 g per 1000 calories and partic- all risk reductions in developing diabetes was observed in the Met-
ipating in at least 30 minutes a day of physical activity. Participants formin group.
received seven individual sessions with the nutritionist during the In addition to decreasing the risk of developing diabetes, most
first year and one session every 3 months thereafter. They also re- of the studies also documented improvements in other clinical
ceived individually tailored guidance on increasing physical activity. outcomes such as blood pressure, lipids, and participants required
In this 3-year study, the incidence of progressing to diabetes was dose reductions in blood pressure and lipid medications.
11% in the lifestyle intervention group and 23% in the control For overweight patients with a family history of type 2 diabetes
group. This equaled a 58% reduction in risk of developing diabetes or CVD, assessment of risk and measurement of fasting glucose