Page 61 - untitled
P. 61
AAAC26 21/5/05 10:45 AM Page 60
26 The pelvic viscera
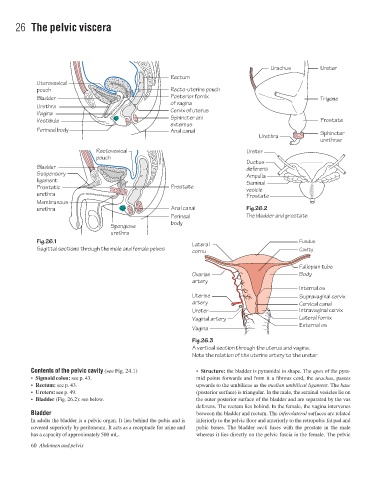
Urachus Ureter
Rectum
Uterovesical
pouch Recto-uterine pouch
Bladder Posterior fornix Trigone
of vagina
Urethra
Cervix of uterus
Vagina
Sphincter ani
Vestibule Prostate
externus
Perineal body Anal canal
Urethra Sphincter
urethrae
Rectovesical Ureter
pouch
Ductus
Bladder deferens
Suspensory Ampulla
ligament Seminal
Prostatic Prostate vesicle
urethra Prostate
Membranous
urethra Anal canal Fig.26.2
Perineal The bladder and prostate
body
Spongiose
urethra
Fig.26.1 Fundus
Lateral
Sagittal sections through the male and female pelves Cavity
cornu
Fallopian tube
Ovarian Body
artery
Internal os
Uterine Supravaginal cervix
artery Cervical canal
Ureter Intravaginal cervix
Vaginal artery Lateral fornix
External os
Vagina
Fig.26.3
A vertical section through the uterus and vagina.
Note the relation of the uterine artery to the ureter
Contents of the pelvic cavity (see Fig. 24.1) • Structure: the bladder is pyramidal in shape. The apex of the pyra-
• Sigmoid colon: see p. 43. mid points forwards and from it a fibrous cord, the urachus, passes
• Rectum: see p. 43. upwards to the umbilicus as the median umbilical ligament. The base
• Ureters: see p. 49. (posterior surface) is triangular. In the male, the seminal vesicles lie on
• Bladder (Fig. 26.2): see below. the outer posterior surface of the bladder and are separated by the vas
deferens. The rectum lies behind. In the female, the vagina intervenes
Bladder between the bladder and rectum. The inferolateral surfaces are related
In adults the bladder is a pelvic organ. It lies behind the pubis and is inferiorly to the pelvic floor and anteriorly to the retropubic fat pad and
covered superiorly by peritoneum. It acts as a receptacle for urine and pubic bones. The bladder neck fuses with the prostate in the male
has a capacity of approximately 500 mL. whereas it lies directly on the pelvic fascia in the female. The pelvic
60 Abdomen and pelvis