Page 133 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 133
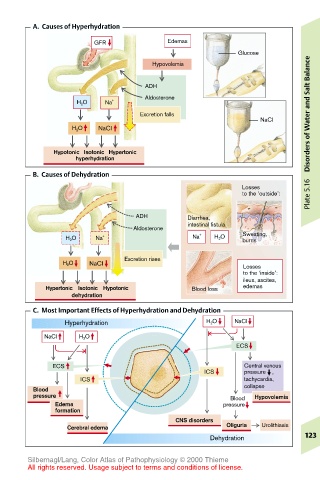
A. Causes of Hyperhydration
GFR Edemas
Glucose
Salt Balance
Hypovolemia
ADH
Aldosterone
H 2 O Na + and
Excretion falls
NaCl
H 2 O NaCl
Hypotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Disorders of Water
hyperhydration
B. Causes of Dehydration
Plate 5.16
Losses
to the ‘outside’:
ADH Diarrhea,
intestinal fistula
Aldosterone
H 2 O Na + Na + H 2 O Sweating,
burns
Excretion rises
H 2 O NaCl Losses
to the ‘inside’:
ileus, ascites,
Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Blood loss edemas
dehydration
C. Most Important Effects of Hyperhydration and Dehydration
Hyperhydration H 2 O NaCl
NaCl H 2 O
ECS
ECS Central venous
ICS pressure ,
ICS tachycardia,
collapse
Blood
pressure Blood Hypovolemia
Edema pressure
formation
CNS disorders
Cerebral edema Oliguria Urolithiasis
Dehydration 123
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.