Page 169 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 169
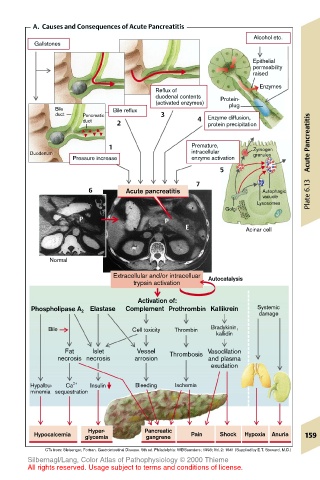
A. Causes and Consequences of Acute Pancreatitis
Alcohol etc.
Gallstones
Epithelial
permeability
raised
Enzymes
Reflux of
duodenal contents Protein-
(activated enzymes) plug
Bile Bile reflux
duct Pancreatic 3
duct 4 Enzyme diffusion,
2 protein precipitation Pancreatitis
1 Premature, Zymogen
Duodenum intracellular granules
Pressure increase enzyme activation Acute
5
7
6 Acute pancreatitis Autophagic
vacuole Plate 6.13
Lysosomes
Golgi
P P
E Acinar cell
Normal
Extracellular and/or intracelluar Autocatalysis
trypsin activation
Activation of:
Phospholipase A 2 Elastase Complement Prothrombin Kallikrein Systemic
damage
Bile Cell toxicity Thrombin Bradykinin,
kallidin
Fat Islet Vessel Thrombosis Vasodilation
necrosis necrosis arrosion and plasma
exudation
Hypalbu- Ca 2+ Insulin Bleeding Ischemia
minemia sequestration
Hyper- Pancreatic
Hypocalcemia glycemia gangrene Pain Shock Hypoxia Anuria 159
CTs from: Sleisenger, Fortran. Gastrointestinal Disease. 5th ed. Philadelphia: WBSaunders; 1993; Vol.2: 1641 (Supplied by E.T. Steward, M.D.)
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.