Page 215 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 215
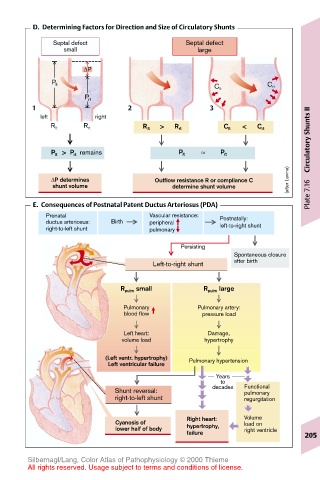
D. Determining Factors for Direction and Size of Circulatory Shunts
Septal defect Septal defect
small large
∆P
P lt C rt
C lt
P rt
1 2 3
left right
> <
R lt R rt R lt R rt C lt C rt
P lt > P rt remains P lt ≈ P rt Circulatory Shunts II
(after Levine)
Outflow resistance R or compliance C
∆P determines
shunt volume determine shunt volume Plate 7.16
E. Consequences of Postnatal Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Prenatal Vascular resistance: Postnatally:
ductus arteriosus: Birth peripheral left-to-right shunt
right-to-left shunt pulmonary
Persisting
Spontaneous closure
Left-to-right shunt after birth
R pulm small R pulm large
Pulmonary Pulmonary artery:
blood flow pressure load
Left heart: Damage,
volume load hypertrophy
(Left ventr. hypertrophy) Pulmonary hypertension
Left ventricular failure
Years
to
Shunt reversal: decades Functional
pulmonary
right-to-left shunt regurgitation
Right heart: Volume
Cyanosis of load on
lower half of body hypertrophy, right ventricle
failure 205
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.