Page 221 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 221
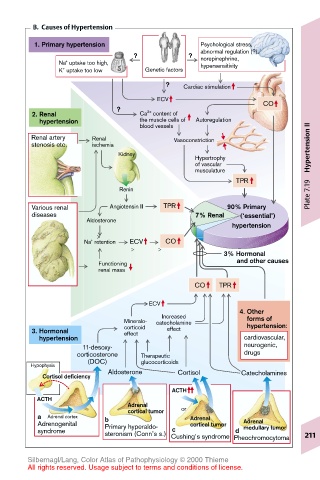
B. Causes of Hypertension
1. Primary hypertension Psychological stress,
abnormal regulation (?),
? ? norepinephrine,
+
Na uptake too high, hypersensitivity
+
K uptake too low Genetic factors
? Cardiac stimulation
ECV
CO
??
2+
2. Renal Ca content of
hypertension the muscle cells of Autoregulation
blood vessels
Renal artery Renal Vasoconstriction
stenosis etc. ischemia Hypertension II
Kidney
Hypertrophy
of vascular
musculature
TPR
Renin Plate 7.19
Various renal Angiotensin II TPR 90% Primary
diseases 7% Renal (‘essential’)
Aldosterone
hypertension
+
Na retention ECV CO
3% Hormonal
and other causes
Functioning
renal mass
CO TPR
ECV
4. Other
Increased
Mineralo- catecholamine forms of
hypertension:
3. Hormonal corticoid effect
effect
hypertension cardiovascular,
11-desoxy- neurogenic,
corticosterone Therapeutic drugs
(DOC) glucocorticoids
Hypophysis
Aldosterone Cortisol Catecholamines
Cortisol deficiency
ACTH
ACTH
Adrenal
cortical tumor or
a Adrenal cortex b Adrenal
Adrenogenital Primary hyperaldo- cortical tumor Adrenal
medullary tumor
c
syndrome steronism (Conn’s s.) Cushing’s syndrome Pheochromocytoma 211
d
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.