Page 49 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 49
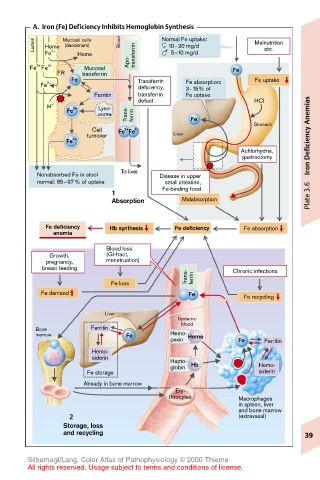
A. Iron (Fe) Deficiency Inhibits Hemoglobin Synthesis
Lumen Heme Mucosal cells Blood Normal Fe uptake: Malnutrition
10–20 mg/d
(duodenum)
etc.
Fe 2+ Heme transferrin 5–10 mg/d
Apo-
2+
Fe Fe 3+ Mucosal Fe
FR transferrin
Fe Transferrin Fe absorption: Fe uptake
Fe 2+ deficiency, 3–15% of
Ferritin transferrin Fe uptake
defect HCI
H + 3+ Lyso-
Fe Anemias
some Trans- ferrin Fe
Stomach
Cell Fe Fe 3+
3+
turnover Liver
Fe 3+
Achlorhydria, Iron Deficiency
gastrectomy
Nonabsorbed Fe in stool To liver Disease in upper
normal: 85–97% of uptake small intestine,
Fe-binding food
1 Plate 3.6
Absorption Malabsorption
Fe deficiency Hb synthesis Fe deficiency Fe absorption
anemia
Blood loss
Growth, (GI-tract,
pregnancy, menstruation)
breast feeding Chronic infections
Trans- ferrin
Fe loss
Fe demand Fe Fe recycling
Liver
Systemic
Bone Ferritin blood
marrow Fe Hemo- Heme
pexin Fe Ferritin
Hemo-
siderin
Hapto-
globin Hb Hemo-
Fe storage siderin
Already in bone marrow
Ery-
throcytes Macrophages
in spleen, liver
and bone marrow
2 (extravasal)
Storage, loss
and recycling 39
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.