Page 51 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 51
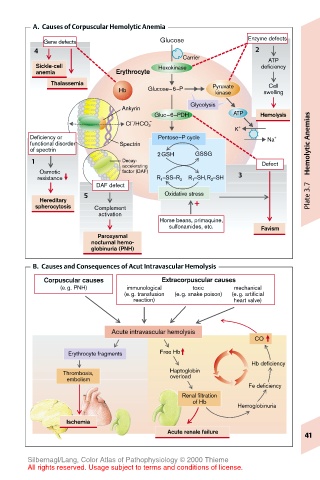
A. Causes of Corpuscular Hemolytic Anemia
Gene defects Glucose Enzyme defects
4 2
Carrier ATP
Sickle-cell Hexokinase deficiency
anemia Erythrocyte
Thalassemia Pyruvate Cell
Hb Glucose–6–P kinase swelling
Glycolysis
Ankyrin
Gluc–6–PDH ATP Hemolysis
– –
Cl /HCO 3 + Anemias
K
Deficiency or Pentose–P cycle Na +
functional disorder Spectrin
of spectrin
2 GSH GSSG
1 Decay- Defect Hemolytic
accelerating
Osmotic factor (DAF)
resistance R 1 –SS–R 2 R 1 –SH,R 2 –SH 3
DAF defect
5 Oxidative stress Plate 3.7
Hereditary +
spherocytosis Complement
activation
Horse beans, primaquine,
sulfonamides, etc. Favism
Paroxysmal
nocturnal hemo-
globinuria (PNH)
B. Causes and Consequences of Acut Intravascular Hemolysis
Corpuscular causes Extracorpuscular causes
(e.g. PNH) immunological toxic mechanical
(e.g. transfusion (e.g. snake poison) (e.g. artificial
reaction) heart valve)
Acute intravascular hemolysis
CO
Erythrocyte fragments Free Hb
Hb deficiency
Thrombosis, Haptoglobin
embolism overload
Fe deficiency
Renal filtration
of Hb
Hemoglobinuria
Ischemia
Acute renale failure
41
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.