Page 67 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 67
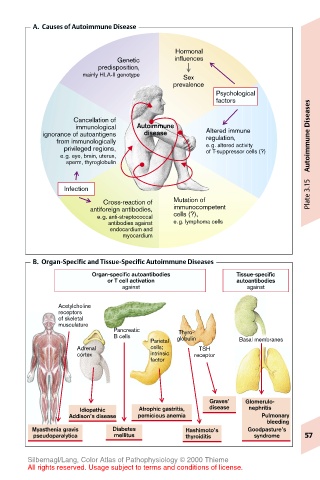
A. Causes of Autoimmune Disease
Hormonal
Genetic influences
predisposition,
mainly HLA-II genotype Sex
prevalence
Psychological
factors
Cancellation of Diseases
immunological Autoimmune
ignorance of autoantigens disease Altered immune
regulation,
from immunologically e.g. altered activity
privileged regions, of T-suppressor cells (?) Autoimmune
e.g. eye, brain, uterus,
sperm, thyroglobulin
Infection Plate 3.15
Cross-reaction of Mutation of
antiforeign antibodies, immunocompetent
e.g. anti-streptococcal cells (?),
antibodies against e.g. lymphoma cells
endocardium and
myocardium
B. Organ-Specific and Tissue-Specific Autoimmune Diseases
Organ-specific autoantibodies Tissue-specific
or T cell activation autoantibodies
against against
Acetylcholine
receptors
of skeletal
musculature
Pancreatic Thyro-
B cells globulin
Parietal Basal membranes
Adrenal cells; TSH
cortex intrinsic receptor
factor
Graves’ Glomerulo-
Idiopathic Atrophic gastritis, disease nephritis
Addison’s disease pernicious anemia Pulmonary
bleeding
Myasthenia gravis Diabetes Hashimoto’s Goodpasture’s
pseudoparalytica mellitus thyroiditis syndrome 57
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.