Page 93 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 93
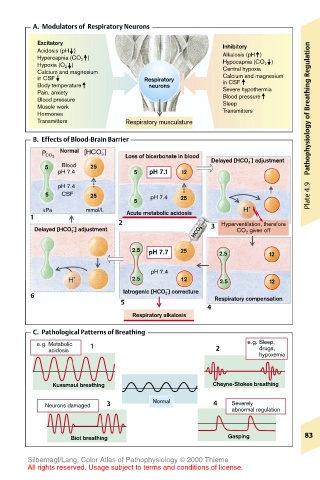
A. Modulators of Respiratory Neurons
Excitatory Inhibitory
Acidosis (pH ) Alkalosis (pH )
Hypercapnia (CO 2 ) Hypocapnia (CO 2 )
Hypoxia (O 2 ) Central hypoxia
Calcium and magnesium
in CSF Respiratory Calcium and magnesium
in CSF
Body temperature neurons Severe hypothermia
Pain, anxiety Blood pressure
Blood pressure Sleep
Muscle work Transmitters Pathophysiology of Breathing Regulation
Hormones
Transmitters Respiratory musculature
B. Effects of Blood-Brain Barrier
–
Normal [HCO 3 ]
Loss of bicarbonate in blood Delayed [HCO 3 ] adjustment
P CO 2
–
5 Blood 25
pH 7.4 5 pH 7.1 12
pH 7.4
5 CSF 25 pH 7.4 25 Plate 4.9
5
kPa mmol/L Acute metabolic acidosis H +
1
2 – Hyperventilation, therefore
–
Delayed [HCO 3 ] adjustment 3 CO 2 given off
HCO 3
2.5 pH 7.7 25 2.5 12
pH 7.4
H + 2.5 12 2.5 12
–
Iatrogenic [HCO 3 ] correcture
6 Respiratory compensation
5
4
Respiratory alkalosis
C. Pathological Patterns of Breathing
e.g. Metabolic 1 e.g. Sleep,
acidosis 2 drugs,
hypoxemia
Kussmaul breathing Cheyne-Stokes breathing
Neurons damaged 3 Normal 4 Severely
abnormal regulation
Biot breathing Gasping 83
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.