Page 95 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 95
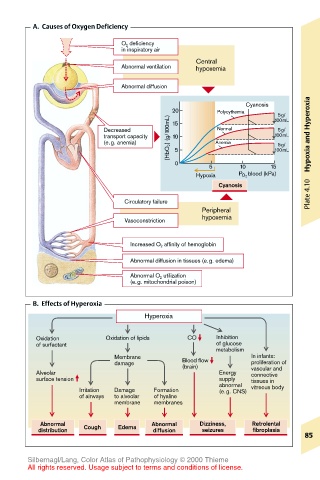
A. Causes of Oxygen Deficiency
O 2 deficiency
in inspiratory air
Central
Abnormal ventilation hypoxemia
Abnormal diffusion
Cyanosis
20 Polycythemia 5g/ Hyperoxia
[HbO 2 ] (g/100mL)
Decreased 15 Normal 100mL
5g/
transport capacity 10 100mL
(e.g. anemia) 5 Anemia 100mL Hypoxia and
5g/
0
5 10 15
Hypoxia P O 2 blood (kPa)
Cyanosis
Circulatory failure Plate 4.10
Peripheral
hypoxemia
Vasoconstriction
Increased O 2 affinity of hemoglobin
Abnormal diffusion in tissues (e.g. edema)
Abnormal O 2 utilization
(e.g. mitochondrial poison)
B. Effects of Hyperoxia
Hyperoxia
Oxidation Oxidation of lipids CO Inhibition
of surfactant of glucose
metabolism
Membrane In infants:
damage Blood flow proliferation of
(brain)
Alveolar Energy vascular and
connective
surface tension supply tissues in
abnormal
Irritation Damage Formation (e.g. CNS) vitreous body
of airways to alveolar of hyaline
membrane membranes
Abnormal Abnormal Dizziness, Retrolental
distribution Cough Edema diffusion seizures fibroplasia
85
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.