Page 99 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 99
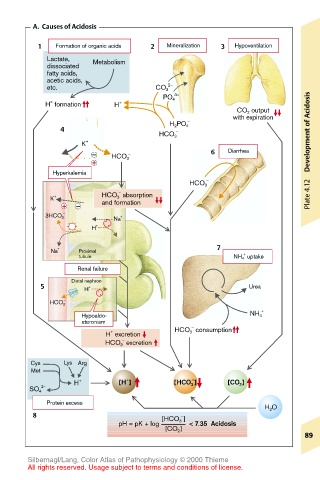
A. Causes of Acidosis
1 Formation of organic acids 2 Mineralization 3 Hypoventilation
Lactate, Metabolism
dissociated
fatty acids,
acetic acids,
etc. CO 3 2–
3–
PO 4
+
H formation H + Acidosis
CO 2 output
with expiration
–
H 2 PO 4
4 –
HCO 3
K + Development of
6 Diarrhea
–
HCO 3
–
Hyperkalemia +
–
HCO 3
–
HCO 3 absorption Plate 4.12
K +
and formation
– + –
Na
3HCO 3 +
H +
Na + Proximal 7
+
tubule NH 4 uptake
Renal failure
Distal nephron
5 H + Urea
–
HCO 3
+
Hypoaldo- NH 4
steronism –
+
H excretion HCO 3 consumption
–
HCO 3 excretion
Cys Lys Arg
Met
+
–
H + [H ] [HCO 3 ] [CO 2 ]
2–
SO 4
Protein excess
H 2 O
8 [HCO 3 ]
–
pH = pK + log < 7.35 Acidosis
[CO 2 ]
89
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.