Page 31 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 31
8 S C O P E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
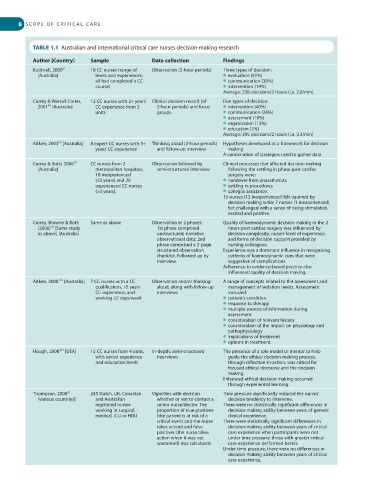
TABLE 1.1 Australian and international critical care nurses decision-making research
Author [Country] Sample Data collection Findings
61
Bucknall, 2000 18 CC nurses (range of Observation (2-hour periods) Three types of decision:
[Australia] levels and experiences; ● evaluation (51%)
all had completed a CC ● communication (30%)
course) ● intervention (19%)
Average: 238 decisions/2 hours (i.e. 2.0/min)
Currey & Worrall-Carter, 12 CC nurses with 2+ years’ Clinical decision record (of Five types of decision:
2001 [Australia] CC experience from 3 2-hour periods) and focus ● intervention (40%)
68
units groups ● communication (26%)
● assessment (19%)
● organisation (13%)
● education (2%)
Average: 395 decisions/2 hours (i.e. 3.3/min)
69
Aitken, 2003 [Australia] 8 expert CC nurses with 5+ Thinking aloud (2-hour periods) Hypotheses developed as a framework for decision
years’ CC experience and follow-up interview making
A combination of strategies used to gather data
70
Currey & Botti, 2006 CC nurses from 2 Observation followed by Clinical processes that affected decision making
[Australia] metropolitan hospitals; semi-structured interview following the settling in phase post cardiac
18 inexperienced surgery were:
(≤3 years) and 20 ● handover from anaesthetists
experienced CC nurses ● settling in procedures
(>3 years). ● collegial assistance.
15 nurses (13 inexperienced) felt daunted by
decision making while 7 nurses (1 inexperienced)
felt challenged with a sense of being stimulated,
excited and positive.
Currey, Browne & Botti Same as above Observation in 2 phases: Quality of haemodynamic decision making in the 2
(2006) [Same study 1st phase comprised hours post cardiac surgery was influenced by
70
as above] [Australia] unstructured, narrative decision complexity, nurses’ level of experience,
observational data; 2nd and forms of decision support provided by
phase comprised a 2-page nursing colleagues.
structured observation Experience was a dominant influence in recognising
checklist. Followed up by patterns of haemodynamic cues that were
interview. suggestive of complications.
Adherence to evidence-based practice also
influenced quality of decision making.
Aitken, 2008 [Australia] 7 CC nurses with a CC Observation and/or thinking A range of concepts related to the assessment and
102
qualification, >5 years aloud, along with follow-up management of sedation needs. Assessment
CC experience, and interviews included:
working ≥2 days/week ● patient’s condition
● response to therapy
● multiple sources of information during
assessment
● consideration of relevant history
● consideration of the impact on physiology and
pathophysiology
● implications of treatment
● options in treatment.
103
Hough, 2008 [USA] 15 CC nurses from 4 units, In-depth, semi-structured The presence of a role model or mentor to help
with varied experience interviews guide the ethical decision-making process,
and education levels through reflection-in-action, was critical for
focused ethical discourse and the decision
making.
Enhanced ethical decision making occurred
through experiential learning.
67
Thompson, 2008 245 Dutch, UK, Canadian Vignettes with decision Time pressure significantly reduced the nurses’
[various countries] and Australian whether or not to contact a decision tendency to intervene.
registered nurses senior nurse/doctor. The There were no statistically significant differences in
working in surgical, proportion of true positives decision-making ability between years of generic
medical, ICU or HDU (the patient is at risk of a clinical experience.
critical event and the nurse There were statistically significant differences in
takes action) and false decision-making ability between years of critical
positives (the nurse takes care experience when participants were not
action when it was not under time pressure: those with greater critical
warranted) was calculated. care experience performed better.
Under time pressure, there were no differences in
decision-making ability between years of critical
care experience.