Page 550 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 550
Gastrointestinal, Liver and Nutritional Alterations 527
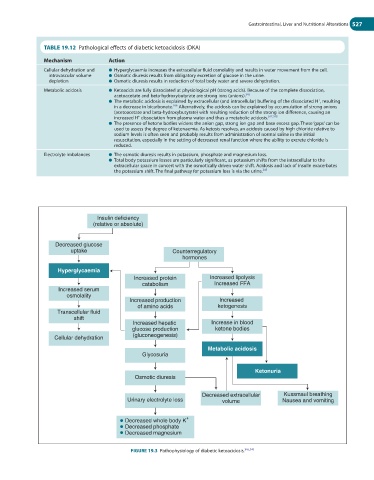
TABLE 19.12 Pathological effects of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Mechanism Action
Cellular dehydration and ● Hyperglycaemia increases the extracellular fluid osmolality and results in water movement from the cell.
intravascular volume ● Osmotic diuresis results from obligatory excretion of glucose in the urine.
depletion ● Osmotic diuresis results in reduction of total body water and severe dehydration.
Metabolic acidosis ● Ketoacids are fully dissociated at physiological pH (strong acids). Because of the complete dissociation,
acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are strong ions (anions). 345
● The metabolic acidosis is explained by extracellular (and intracellular) buffering of the dissociated H , resulting
+
in a decrease in bicarbonate. Alternatively, the acidosis can be explained by accumulation of strong anions
166
(acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate) with resulting reduction of the strong ion difference, causing an
+
increased H dissociation from plasma water and thus a metabolic acidosis. 347,348
● The presence of ketone bodies widens the anion gap, strong ion gap and base excess gap. These ‘gaps’ can be
used to assess the degree of ketonaemia. As ketosis resolves, an acidosis caused by high chloride relative to
sodium levels is often seen and probably results from administration of normal saline in the initial
resuscitation, especially in the setting of decreased renal function where the ability to excrete chloride is
reduced.
Electrolyte imbalances ● The osmotic diuresis results in potassium, phosphate and magnesium loss.
● Total body potassium losses are particularly significant, as potassium shifts from the intracellular to the
extracellular space in concert with the osmotically driven water shift. Acidosis and lack of insulin exacerbates
the potassium shift. The final pathway for potassium loss is via the urine. 345
Insulin deficiency
(relative or absolute)
Decreased glucose
uptake Counterregulatory
hormones
Hyperglycaemia
Increased protein Increased lipolysis
catabolism Increased FFA
Increased serum
osmolality
Increased production Increased
of amino acids ketogenesis
Transcellular fluid
shift
Increased hepatic Increase in blood
glucose production ketone bodies
Cellular dehydration (gluconeogenesis)
Metabolic acidosis
Glycosuria
Ketonuria
Osmotic diuresis
Decreased extracellular Kussmaul breathing
Urinary electrolyte loss volume Nausea and vomiting
+
Decreased whole body K
Decreased phosphate
Decreased magnesium
FIGURE 19.3 Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis. 345,349