Page 545 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 545
522 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
reduced overall hospital length of stay. Survival rates of
all patients who have undergone liver transplantation
exceed 80% at 5 years, 283 with children having superior
survival rates to adults. 282
INDICATIONS FOR TRANSPLANTATION
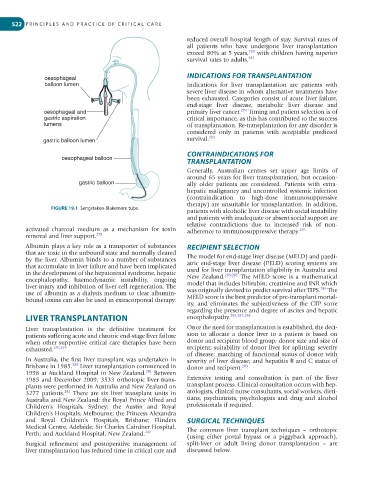
oesophageal
balloon lumen Indications for liver transplantation are patients with
severe liver disease in whom alternative treatments have
been exhausted. Categories consist of acute liver failure,
end-stage liver disease, metabolic liver disease and
oesophageal and primary liver cancer. 284 Timing and patient selection is of
gastric aspiration critical importance, as this has contributed to the success
lumens of transplantation. Re-transplantation for any disorder is
considered only in patients with acceptable predicted
gastric balloon lumen survival. 283
CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR
oesophageal balloon
TRANSPLANTATION
Generally, Australian centres set upper age limits of
around 65 years for liver transplantation, but occasion-
gastric balloon ally older patients are considered. Patients with extra-
hepatic malignancy and uncontrolled systemic infection
(contraindication to high-dose immunosuppressive
therapy) are unsuitable for transplantation. In addition,
FIGURE 19.1 Sengstaken-Blakemore tube.
patients with alcoholic liver disease with social instability
and patients with inadequate or absent social support are
relative contradictions due to increased risk of non-
activated charcoal medium as a mechanism for toxin adherence to immunosuppressive therapy. 283
removal and liver support. 278
Albumin plays a key role as a transporter of substances RECIPIENT SELECTION
that are toxic in the unbound state and normally cleared
by the liver. Albumin binds to a number of substances The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and paedi-
that accumulate in liver failure and have been implicated atric end-stage liver disease (PELD) scoring systems are
in the development of the hepatorenal syndrome, hepatic used for liver transplantation eligibility in Australia and
283,285
encephalopathy, haemodynamic instability, ongoing New Zealand. The MELD score is a mathematical
liver injury and inhibition of liver cell regeneration. The model that includes bilirubin, creatinine and INR which
286
use of albumin as a dialysis medium to clear albumin- was originally devised to predict survival after TIPS. The
bound toxins can also be used in extracorporeal therapy. MELD score is the best predictor of pre-transplant mortal-
ity, and eliminates the subjectiveness of the CTP score
regarding the presence and degree of ascites and hepatic
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION encephalopathy. 285,287,288
Liver transplantation is the definitive treatment for Once the need for transplantation is established, the deci-
patients suffering acute and chronic end-stage liver failure sion to allocate a donor liver to a patient is based on
when other supportive critical care therapies have been donor and recipient blood group; donor size and size of
exhausted. 250,279 recipient; suitability of donor liver for splitting; severity
of disease; matching of functional status of donor with
In Australia, the first liver transplant was undertaken in severity of liver disease; and hepatitis B and C status of
Brisbane in 1985. 280 Liver transplantation commenced in donor and recipient. 283
281
1998 at Auckland Hospital in New Zealand. Between
1985 and December 2009, 3533 orthotopic liver trans- Extensive testing and consultation is part of the liver
plants were performed in Australia and New Zealand on transplant process. Clinical consultation occurs with hep-
3277 patients. 282 There are six liver transplant units in atologists, clinical nurse consultants, social workers, dieti-
Australia and New Zealand: the Royal Prince Alfred and tians, psychiatrists, psychologists and drug and alcohol
Children’s Hospitals, Sydney; the Austin and Royal professionals if required.
Children’s Hospitals, Melbourne; the Princess Alexandra
and Royal Children’s Hospitals, Brisbane; Flinders SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
Medical Centre, Adelaide; Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital, The common liver transplant techniques – orthotopic
Perth; and Auckland Hospital, New Zealand. 282
(using either portal bypass or a piggyback approach),
Surgical refinement and postoperative management of split-liver or adult living donor transplantation – are
liver transplantation has reduced time in critical care and discussed below.