Page 670 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 670
Trauma Management 647
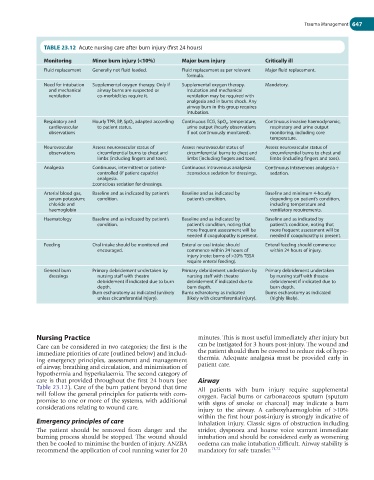
TABLE 23.12 Acute nursing care after burn injury (first 24 hours)
Monitoring Minor burn injury (<10%) Major burn injury Critically ill
Fluid replacement Generally not fluid loaded. Fluid replacement as per relevant Major fluid replacement.
formula.
Need for intubation Supplemental oxygen therapy. Only if Supplemental oxygen therapy. Mandatory.
and mechanical airway burns are suspected or Intubation and mechanical
ventilation co-morbidities require it. ventilation may be required with
analgesia and in burns shock. Any
airway burn in this group requires
intubation.
Respiratory and Hourly TPR, BP, SpO 2 adapted according Continuous ECG, SpO 2 , temperature, Continuous invasive haemodynamic,
cardiovascular to patient status. urine output (hourly observations respiratory and urine output
observations if not continuously monitored). monitoring, including core
temperature.
Neurovascular Assess neurovascular status of Assess neurovascular status of Assess neurovascular status of
observations circumferential burns to chest and circumferential burns to chest and circumferential burns to chest and
limbs (including fingers and toes). limbs (including fingers and toes). limbs (including fingers and toes).
Analgesia Continuous, intermittent or patient- Continuous intravenous analgesia Continuous intravenous analgesia +
controlled (if patient capable) ±conscious sedation for dressings. sedation.
analgesia.
±conscious sedation for dressings.
Arterial blood gas, Baseline and as indicated by patient’s Baseline and as indicated by Baseline and minimum 4-hourly
serum potassium; condition. patient’s condition. depending on patient’s condition,
chloride and including temperature and
haemoglobin ventilatory requirements.
Haematology Baseline and as indicated by patient’s Baseline and as indicated by Baseline and as indicated by
condition. patient’s condition, noting that patient’s condition, noting that
more frequent assessment will be more frequent assessment will be
needed if coagulopathy is present. needed if coagulopathy is present.
Feeding Oral intake should be monitored and Enteral or oral intake should Enteral feeding should commence
encouraged. commence within 24 hours of within 24 hours of injury.
injury (note: burns of >20% TBSA
require enteral feeding).
General burn Primary debridement undertaken by Primary debridement undertaken by Primary debridement undertaken
dressings nursing staff with theatre nursing staff with theatre by nursing staff with theatre
debridement if indicated due to burn debridement if indicated due to debridement if indicated due to
depth. burn depth. burn depth.
Burn escharotomy as indicated (unlikely Burns echarotomy as indicated Burns escharotomy as indicated
unless circumferential injury). (likely with circumferential injury). (highly likely).
Nursing Practice minutes. This is most useful immediately after injury but
Care can be considered in two categories; the first is the can be instigated for 3 hours post-injury. The wound and
immediate priorities of care (outlined below) and includ- the patient should then be covered to reduce risk of hypo-
ing emergency principles, assessment and management thermia. Adequate analgesia must be provided early in
of airway, breathing and circulation, and minimisation of patient care.
hypothermia and hyperkalaemia. The second category of
care is that provided throughout the first 24 hours (see Airway
Table 23.12). Care of the burn patient beyond that time All patients with burn injury require supplemental
will follow the general principles for patients with com- oxygen. Facial burns or carbonaceous sputum (sputum
promise to one or more of the systems, with additional with signs of smoke or charcoal) may indicate a burn
considerations relating to wound care. injury to the airway. A carboxyhaemoglobin of >10%
within the first hour post-injury is strongly indicative of
Emergency principles of care inhalation injury. Classic signs of obstruction including
The patient should be removed from danger and the stridor, dyspnoea and hoarse voice warrant immediate
burning process should be stopped. The wound should intubation and should be considered early as worsening
then be cooled to minimise the burden of injury. ANZBA oedema can make intubation difficult. Airway stability is
recommend the application of cool running water for 20 mandatory for safe transfer. 71,72