Page 773 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 773
750 S P E C I A LT Y P R A C T I C E I N C R I T I C A L C A R E
Blood flow
ceases in
RICA
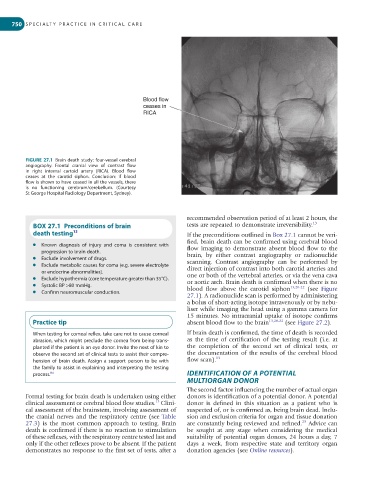
FIGURE 27.1 Brain death study: four-vessel cerebral
angiography. Frontal cranial view of contrast flow
in right internal cartoid artery (RICA). Blood flow
ceases at the carotid siphon. Conclusion: if blood
flow is shown to have ceased in all the vessels, there
is no functioning cerebrum/cerebellum. (Courtesy
St George Hospital Radiology Department, Sydney).
recommended observation period of at least 2 hours, the
BOX 27.1 Preconditions of brain tests are repeated to demonstrate irreversibility. 13
death testing 13 If the preconditions outlined in Box 27.1 cannot be veri-
fied, brain death can be confirmed using cerebral blood
l Known diagnosis of injury and coma is consistent with flow imaging to demonstrate absent blood flow to the
progression to brain death. brain, by either contrast angiography or radionuclide
l Exclude involvement of drugs. scanning. Contrast angiography can be performed by
l Exclude metabolic causes for coma (e.g. severe electrolyte direct injection of contrast into both carotid arteries and
or endocrine abnormalities). one or both of the vertebral arteries, or via the vena cava
l Exclude hypothermia (core temperature greater than 35°C). or aortic arch. Brain death is confirmed when there is no
l Systolic BP >80 mmHg. blood flow above the carotid siphon 13,20-22 (see Figure
l Confirm neuromuscular conduction.
27.1). A radionuclide scan is performed by administering
a bolus of short-acting isotope intravenously or by nebu-
liser while imaging the head using a gamma camera for
15 minutes. No intracranial uptake of isotope confirms
Practice tip absent blood flow to the brain 13,20-22 (see Figure 27.2).
When testing for corneal reflex, take care not to cause corneal If brain death is confirmed, the time of death is recorded
abrasion, which might preclude the cornea from being trans- as the time of certification of the testing result (i.e. at
planted if the patient is an eye donor. Invite the next of kin to the completion of the second set of clinical tests, or
observe the second set of clinical tests to assist their compre- the documentation of the results of the cerebral blood
hension of brain death. Assign a support person to be with flow scan). 13
the family to assist in explaining and interpreting the testing
process. 84 IDENTIFICATION OF A POTENTIAL
MULTIORGAN DONOR
The second factor influencing the number of actual organ
Formal testing for brain death is undertaken using either donors is identification of a potential donor. A potential
13
clinical assessment or cerebral blood flow studies. Clini- donor is defined in this situation as a patient who is
cal assessment of the brainstem, involving assessment of suspected of, or is confirmed as, being brain dead. Inclu-
the cranial nerves and the respiratory centre (see Table sion and exclusion criteria for organ and tissue donation
23
27.3) is the most common approach to testing. Brain are constantly being reviewed and refined. Advice can
death is confirmed if there is no reaction to stimulation be sought at any stage when considering the medical
of these reflexes, with the respiratory centre tested last and suitability of potential organ donors, 24 hours a day, 7
only if the other reflexes prove to be absent. If the patient days a week, from respective state and territory organ
demonstrates no response to the first set of tests, after a donation agencies (see Online resources).