Page 774 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 774
Organ Donation and Transplantation 751
TABLE 27.3 Clinical brain death testing 13,38
Test Cranial nerves/neurological function Test technique Outcome
1. Response to Trigeminal V (sensory), Facial VII (motor) Stimulus within the cranial nerve If reflex is absent, the patient
painful stimuli distribution (e.g. firm pressure over will not grimace or react.
supraorbital region)
2. Pupillary response Optic II, Oculomotor III Using torch If reflex is absent, the pupils
to light are fixed: may or may not be
dilated.
3. Corneal reflex Trigeminal V (sensory), Facial VII (motor) Using wisp of cotton wool to touch the If the reflex is absent, the eyes
cornea will not react or blink.
4. Gag reflex Glossopharyngeal IX, Vagus X Using a tongue depressor on the If reflex is absent, there is no
oropharynx or moving ETT gag or pharyngeal response.
5. Cough reflex Glossopharyngeal IX, Vagus X Using suction catheter down ETT to If reflex is absent, there is no
deliberately stimulate the carina cough response.
6. Oculovestibular Vestibulocochlear VII, Oculomotor III, Checking first that both tympanic If reflex is absent, the eyes
reflex Abducens VI membranes are intact or not remain fixed rather than
obstructed; then slowly irrigating both deviating towards the
ears with 50 mL iced water while eyes stimulus.
are held open
7. Apnoea test Medullar respiratory centre Last test to be performed when all other The period of time
reflexes have proven to be absent. disconnected from the
The patient is preoxygenated on 100% ventilator must be long
O 2 , an ABG analysis is performed to enough for the arterial
ascertain the baseline CO 2 , then carbon monoxide level to
the patient is disconnected from rise to a threshold high
mechanical ventilation but supplied enough to normally
with oxygen via catheter or T piece; stimulate respiration, i.e. an
the patient is observed for signs of arterial CO 2 >60 mmHg and
respiratory effort an arterial pH of <7.30.
8. Oculocephalic Ocular function and internuclear pathway Although not a formal component of If the reflex is absent, the eyes
reflex (doll’s eyes) in brainstem for Cranial Nerves III, IV, VI; brain death testing, this reflex may be will move with the head and
labyrinthine semicircular canals, otoliths tested as routine practice. The test must do not move within their
and neck muscle proprioceptors not be performed if an unstable orbit, indicating significant
cervical spine is suspected. Holding the brainstem injury.
eyes open, rotate the head from side to
side, observing the position of the eyes.
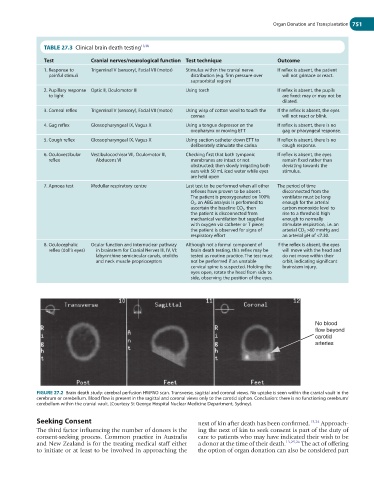
No blood
flow beyond
carotid
arteries
FIGURE 27.2 Brain death study: cerebral perfusion HMPAO scan. Transverse, sagittal and coronal views. No uptake is seen within the cranial vault in the
cerebrum or cerebellum. Blood flow is present in the sagittal and coronal views only to the carotid siphon. Conclusion: there is no functioning cerebrum/
cerebellum within the cranial vault. (Courtesy St George Hospital Nuclear Medicine Department, Sydney).
Seeking Consent next of kin after death has been confirmed. 13,24 Approach-
The third factor influencing the number of donors is the ing the next of kin to seek consent is part of the duty of
consent-seeking process. Common practice in Australia care to patients who may have indicated their wish to be
and New Zealand is for the treating medical staff either a donor at the time of their death. 13,25,26 The act of offering
to initiate or at least to be involved in approaching the the option of organ donation can also be considered part