Page 1148 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1148
Chapter 64 Pathobiology of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia 1007
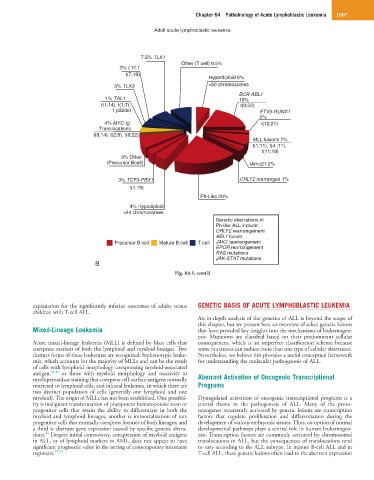
Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia
7.5% TLX1
Other (T cell) 9.5%
2% LYL1
t(7;19)
Hyperdiploid 6%
3% TLX3 >50 chromosomes
BCR-ABL1
1% TAL1 19%
t(1;14), t(1;7), t(9;22)
1 p32del ETV6-RUNX1
2%
4% MYC-Ig t(12;21)
Translocations
t(8;14), t(2;8), t(8;22)
MLL fusions 7%
t(1;11), t(4 ;11),
t(11;19)
9% Other
(Precursor Bcell) iAmp21 2%
3% TCF3-PBX1 CRLF2 rearranged 1%
t(1;19)
Ph-Like 20%
4% Hypodiploid
<44 chromosomes
Genetic aberrations in
Ph-like ALL include:
CRLF2 rearrangement
ABL1 fusion
Precursor B cell Mature B cell T cell JAK2 rearrangement
EPOR rearrangement
RAS mutations
JAK-STAT mutations
B
Fig. 64.1, cont’d
explanation for the significantly inferior outcomes of adults versus GENETIC BASIS OF ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
children with T-cell ALL.
An in-depth analysis of the genetics of ALL is beyond the scope of
this chapter, but we present here an overview of select genetic lesions
Mixed-Lineage Leukemia that have provided key insights into the mechanisms of leukemogen-
esis. Mutations are classified based on their predominant cellular
Acute mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) is defined by blast cells that consequences, which is an imperfect classification scheme because
coexpress markers of both the lymphoid and myeloid lineages. Two some mutations can induce more than one type of cellular aberration.
distinct forms of these leukemias are recognized: biphenotypic leuke- Nevertheless, we believe this provides a useful conceptual framework
mia, which accounts for the majority of MLLs and can be the result for understanding the molecular pathogenesis of ALL.
of cells with lymphoid morphology coexpressing myeloid-associated
antigen, 42,43 or those with myeloid morphology and reactivity to
myeloperoxidase staining that coexpress cell-surface antigens normally Aberrant Activation of Oncogenic Transcriptional
restricted to lymphoid cells, and bilineal leukemia, in which there are Programs
two distinct population of cells (generally one lymphoid and one
myeloid). The origin of MLLs has not been established. One possibil- Dysregulated activation of oncogenic transcriptional programs is a
ity is malignant transformation of pluripotent hematopoietic stem or central theme in the pathogenesis of ALL. Many of the proto-
progenitor cells that retain the ability to differentiate in both the oncogenes recurrently activated by genetic lesions are transcription
myeloid and lymphoid lineages; another is immortalization of rare factors that regulate proliferation and differentiation during the
progenitor cells that normally coexpress features of both lineages; and development of various embryonic tissues. Thus, co-option of normal
a third is aberrant gene expression caused by specific genetic altera- developmental pathways plays a central role in human leukemogen-
44
tions. Despite initial controversy, coexpression of myeloid antigens esis. Transcription factors are commonly activated by chromosomal
in ALL, or of lymphoid markers in AML, does not appear to have translocations in ALL, but the consequences of translocations tend
significant prognostic value in the setting of contemporary treatment to vary according to the ALL subtype. In mature B-cell ALL and in
regimens. 45–47 T-cell ALL, these genetic lesions often lead to the aberrant expression