Page 117 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 117
88 Part I Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology
Oxidative stressors Hb
Drugs (Dose, schedule of “Damaging” variants in
administration), fava 2 the G6PD gene
beans, infections
Met-Hb
GSSG NADPH 6PG
H O
2
Glutathion 1
production GSR G6PD
GPX
H 2 O 2 GSH
ROS NADP G6P
Damage of erythrocytes
Acute hemolytic anemia (AHA)
Tissue hypoxia
Co-morbidities 3
Malaria, ALL,
methemoglobinemia
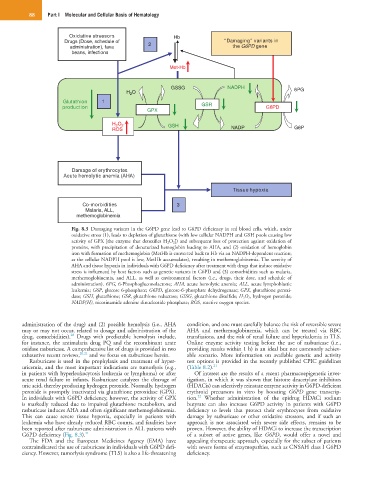
Fig. 8.3 Damaging variants in the G6PD gene lead to G6PD deficiency in red blood cells, which, under
oxidative stress (1), leads to depletion of glutathione (with low cellular NADPH and GSH pools causing low
activity of GPX [the enzyme that detoxifies H 2O 2]) and subsequent loss of protection against oxidation of
proteins, with precipitation of denaturized hemoglobin leading to AHA, and (2) oxidation of hemoglobin
iron with formation of methemoglobin (MetHb is converted back to Hb via an NADPH-dependent reaction;
as the cellular NADPH pool is low, MetHb accumulates), resulting in methemoglobinemia. The severity of
AHA and tissue hypoxia in individuals with G6PD deficiency after treatment with drugs that induce oxidative
stress is influenced by host factors such as genetic variants in G6PD and (3) comorbidities such as malaria,
methemoglobinemia, and ALL, as well as environmental factors (i.e., drugs, their dose, and schedule of
administration). 6PG, 6-Phosphogluconolactone; AHA, acute hemolytic anemia; ALL, acute lymphoblastic
leukemia; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GPX, glutathione peroxi-
dase; GSH, glutathione; GSR, glutathione reductase; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; H 2 O 2, hydrogen peroxide;
NADP(H), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
administration of the drug) and (2) possible hemolysis (i.e., AHA condition, and one must carefully balance the risk of reversible severe
may or may not occur, related to dosage and administration of the AHA and methemoglobinemia, which can be treated via RBC
20
drug, comorbidities). Drugs with predictable hemolysis include, transfusions, and the risk of renal failure and hyperkalemia in TLS.
for instance, the antimalaria drug PQ and the recombinant urate Online enzyme activity testing before the use of rasburicase (i.e.,
oxidase rasburicase. A comprehensive list of drugs is provided in two providing results within 1 h) is an ideal but not commonly achiev-
exhaustive recent reviews, 20,21 and we focus on rasburicase herein. able scenario. More information on available genetic and activity
Rasburicase is used in the prophylaxis and treatment of hyper- test options is provided in the recently published CPIC guidelines
uricemia, and the most important indications are tumorlysis (e.g., (Table 8.2). 21
in patients with hyperleukocytosis leukemia or lymphoma) or after Of interest are the results of a recent pharmacoepigenetic inves-
acute renal failure in infants. Rasburicase catalyzes the cleavage of tigation, in which it was shown that histone deacetylase inhibitors
uric acid, thereby producing hydrogen peroxide. Normally, hydrogen (HDACis) can selectively reinstate enzyme activity in G6PD-deficient
peroxide is promptly inactivated via glutathione peroxidase (GPX). erythroid precursors in vitro by boosting G6PD gene transcrip-
22
In individuals with G6PD deficiency, however, the activity of GPX tion. Whether administration of the epidrug HDACi sodium
is markedly reduced due to impaired glutathione metabolism, and butyrate can also increase G6PD activity in patients with G6PD
rasburicase induces AHA and often significant methemoglobinemia. deficiency to levels that protect their erythrocytes from oxidative
This can cause severe tissue hypoxia, especially in patients with damage by rasburicase or other oxidative stressors, and if such an
leukemia who have already reduced RBC counts, and fatalities have approach is not associated with severe side effects, remains to be
been reported after rasburicase administration in ALL patients with proven. However, the ability of HDACi to increase the transcription
G6PD deficiency (Fig. 8.3). 21 of a subset of active genes, like G6PD, would offer a novel and
The FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have appealing therapeutic approach, especially for the subset of patients
contraindicated the use of rasburicase in individuals with G6PD defi- with severe forms of enzymopathies, such as CNSAH class I G6PD
ciency. However, tumorlysis syndrome (TLS) is also a life-threatening deficiency.