Page 1821 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1821
Chapter 106 Haploidentical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation 1623
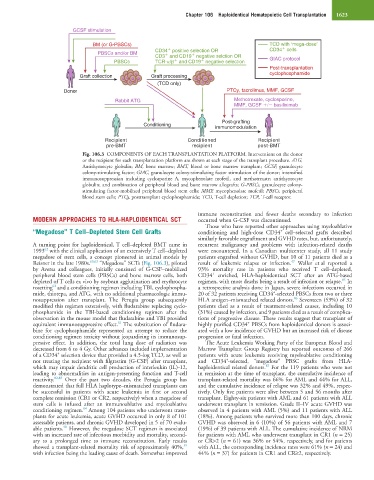
GCSF stimulation
BM (or G-PBSCs) TCD with ‘mega-dose’
CD34 positive selection OR CD34 cells
PBSCs and/or BM
CD3 and CD19 negative selction OR GIAC protocol
PBSCs TCR- / and CD19 negative selection
Post-transplantation
cyclophosphamide
Graft collection Graft processing
(TCD only)
Donor PTCy, tacrolimus, MMF, GCSF
Rabbit ATG Methotrexate, cyclosporine,
MMF, GCSF basiliximab
Post-grafting
Conditioning
immunomodulation
Recipient Conditioned Recipient
pre-BMT recipient post-BMT
Fig. 106.3 COMPONENTS OF EACH TRANSPLANTATION PLATFORM. Interventions on the donor
or the recipient for each transplantation platform are shown at each stage of the transplant procedure. ATG,
Antithymocyte globulin; BM, bone marrow; BMT, blood or bone marrow transplant; GCSF, granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor; GIAC, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor stimulation of the donor; intensified
immunosuppression including cyclosporine A, mycophenolate mofetil, and methotrexate; antithymocyte
globulin; and combination of peripheral blood and bone marrow allografts; G-PBSCs, granulocyte colony-
stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; PBSCs, peripheral
blood stem cells; PTCy, posttransplant cyclophosphamide; TCD, T-cell depletion; TCR, T-cell receptor.
immune reconstitution and fewer deaths secondary to infection
MODERN APPROACHES TO HLA-HAPLOIDENTICAL SCT occurred when G-CSF was discontinued.
Those who have reported other approaches using myeloablative
“Megadose” T Cell–Depleted Stem Cell Grafts conditioning and high-dose CD34 cell–selected grafts described
+
similarly favorable engraftment and GVHD rates, but, unfortunately,
A turning point for haploidentical, T cell–depleted BMT came in recurrent malignancy and problems with infection-related deaths
62
1993 with the clinical application of an extensively T cell–depleted were encountered. In a Canadian multicenter study, all 11 study
megadose of stem cells, a concept pioneered in animal models by patients engrafted without GVHD, but 10 of 11 patients died as a
47
Reisner in the late 1980s. 60,63 “Megadose” SCTs (Fig. 106.3), piloted result of leukemic relapse or infection. Waller et al reported a
by Aversa and colleagues, initially consisted of G-CSF–mobilized 93% mortality rate in patients who received T cell–depleted,
+
peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) and bone marrow cells, both CD34 enriched, HLA-haploidentical SCT after an ATG-based
85
depleted of T cells ex vivo by soybean agglutination and erythrocyte regimen, with most deaths being a result of infection or relapse. In
62
rosetting and a conditioning regimen including TBI, cyclophospha- a retrospective analysis done in Japan, severe infections occurred in
+
mide, thiotepa, and ATG, with no additional pharmacologic immu- 20 of 32 patients receiving CD34 -selected PBSCs from two or three
86
nosuppression after transplant. The Perugia group subsequently HLA antigen–mismatched related donors. Seventeen (53%) of 32
modified this regimen extensively, with fludarabine replacing cyclo- patients died as a result of treatment-related causes, including 10
phosphamide in the TBI-based conditioning regimen after the (31%) caused by infection, and 9 patients died as a result of complica-
observation in the mouse model that fludarabine and TBI provided tions of progressive disease. These results suggest that transplant of
+
81
equivalent immunosuppressive effect. The substitution of fludara- highly purified CD34 PBSCs from haploidentical donors is associ-
bine for cyclophosphamide represented an attempt to reduce the ated with a low incidence of GVHD but an increased risk of disease
conditioning regimen toxicity without jeopardizing its immunosup- progression or fatal infection.
pressive effect. In addition, the total lung dose of radiation was The Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Blood and
decreased from 6 to 4 Gy. Other advances included implementation Marrow Transplant Group Registry has reported outcomes of 266
+
of a CD34 selection device that provided a 4.5-log TCD, as well as patients with acute leukemia receiving myeloablative conditioning
+
not treating the recipient with filgrastim (G-CSF) after transplant, and CD34 -selected, “megadose” PBSC grafts from HLA-
87
which may impair dendritic cell production of interleukin (IL)-12, haploidentical related donors. For the 119 patients who were not
leading to abnormalities in antigen-presenting function and T-cell in remission at the time of transplant, the cumulative incidence of
reactivity. 82,83 Over the past two decades, the Perugia group has transplant-related mortality was 66% for AML and 44% for ALL,
demonstrated that full HLA haplotype–mismatched transplants can and the cumulative incidence of relapse was 32% and 49%, respec-
be successful in patients with acute leukemia in first or second tively. Only five patients were alive between 5 and 56 months after
complete remission (CR1 or CR2, respectively) when a megadose of transplant. Eighty-six patients with AML and 61 patients with ALL
stem cells is infused after an immunoablative and myeloablative underwent transplant in remission. Grade II–IV acute GVHD was
84
conditioning regimen. Among 104 patients who underwent trans- observed in 4 patients with AML (5%) and 11 patients with ALL
plants for acute leukemia, acute GVHD occurred in only 8 of 101 (18%). Among patients who survived more than 100 days, chronic
assessable patients, and chronic GVHD developed in 5 of 70 evalu- GVHD was observed in 6 (10%) of 56 patients with AML and 7
40
able patients. However, the megadose SCT regimen is associated (19%) of 39 patients with ALL. The cumulative incidence of NRM
with an increased rate of infectious morbidity and mortality, second- for patients with AML who underwent transplant in CR1 (n = 25)
ary to a prolonged time to immune reconstitution. Early results or CR>2 (n = 61) was 36% or 54%, respectively, and for patients
39
showed a transplant-related mortality risk of approximately 40%, with ALL, the corresponding incidence rates were 61% (n = 24) and
with infection being the leading cause of death. Somewhat improved 44% (n = 37) for patients in CR1 and CR≥2, respectively.