Page 1911 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1911
Chapter 110 Human Blood Group Antigens and Antibodies 1691
Single-pass proteins
MNSs (GPA/GPB)
Gerbich (GPC/GPD)
Indian (CD44) GPI-linked proteins
Knops (CR1) Cromer (DAF)
Lutheran (B-CAM) Yt (AChE)
LW (ICAM-4) Dombrock (ART4)
Xg JMH
Sc (ERMAP)
Kell Multipass proteins NH 2
Carbohydrate
NH 2 COOH Rh (12 pass)
ABO RhAg (12 pass)
Hh Kx (10 pass)
Lewis Diego (Band 3, 14 pass)
I Colton (AQP-1, 10 pass)
P1 NH 2 Duffy (7 pass) Kidd (10 pass)
P Outside
COOH NH 2 COOH NH 2 COOH
N-glycan O-glycan GPI-linker
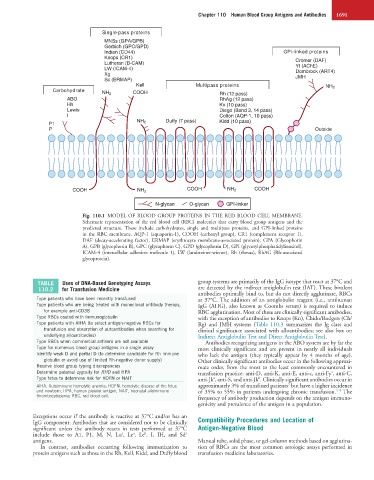
Fig. 110.1 MODEL OF BLOOD GROUP PROTEINS IN THE RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE.
Schematic representation of the red blood cell (RBC) molecules that carry blood group antigens and the
predicted structure. These include carbohydrates, single and multipass proteins, and GPI-linked proteins
in the RBC membrane. AQP-1 (aquaporin-1), COOH (carboxyl group), CR1 (complement receptor 1),
DAF (decay-accelerating factor), ERMAP (erythrocyte membrane-associated protein), GPA (Glycophorin
A), GPB (glycophorin B), GPC (glycophorin C), GPD (glycophorin D), GPI (glycosylphosphatidylinositol),
ICAM-4 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1), LW (landsteiner-wiener), Rh (rhesus), RhAG (Rh-associated
glycoprotein).
TABLE Uses of DNA-Based Genotyping Assays group systems are primarily of the IgG isotype that react at 37°C and
110.2 for Transfusion Medicine are detected by the indirect antiglobulin test (IAT). These bivalent
antibodies optimally bind to, but do not directly agglutinate, RBCs
Type patients who have been recently transfused at 37°C. The addition of an antiglobulin reagent (i.e., antihuman
Type patients who are being treated with monoclonal antibody therapy, IgG (AHG), also known as Coombs serum) is required to induce
for example anti-CD38 RBC agglutination. Most of these are clinically significant antibodies,
Type RBCs coated with immunoglobulin with the exception of antibodies to Knops (Kn), Chido/Rodgers (Ch/
Type patients with AIHA (to select antigen-negative RBCs for Rg) and JMH systems (Table 110.3 summarizes the Ig class and
transfusion and absorption of autoantibodies when searching for clinical significance associated with alloantibodies; see also box on
underlying alloantibodies) Indirect Antiglobulin Test and Direct Antiglobulin Test).
Type RBCs when commercial antisera are not available Antibodies recognizing antigens in the ABO system are by far the
Type for numerous blood group antigens in a single assay most clinically significant and are present in nearly all individuals
Identify weak D and partial D (to determine candidate for Rh immune who lack the antigen (they typically appear by 4 months of age).
globulin or avoid use of limited Rh-negative donor supply) Other clinically significant antibodies occur in the following approxi-
Resolve blood group typing discrepancies mate order, from the most to the least commonly encountered in
Determine paternal zygosity for RHD and HPA transfusion practice: anti-D, anti-K, anti-E, anti-c, anti-Fy , anti-C,
a
Type fetus to determine risk for HDFN or NAIT anti-Jk , anti-S, and anti-Jk . Clinically significant antibodies occur in
b
a
3
AIHA, Autoimmune hemolytic anemia; HDFN, hemolytic disease of the fetus approximately 3% of transfused patients but have a higher incidence
and newborn; HPA, human platelet antigen; NAIT, neonatal alloimmune of 35% to 55% in patients undergoing chronic transfusion. The
4–8
thrombocytopenia; RBC, red blood cell. frequency of antibody production depends on the antigen immuno-
genicity and prevalence of the antigen in a population.
Exceptions occur if the antibody is reactive at 37°C and/or has an
IgG component. Antibodies that are considered not to be clinically Compatibility Procedures and Location of
significant unless the antibody reacts in tests performed at 37°C Antigen-Negative Blood
a
b
a
include those to A1, P1, M, N, Lu , Le , Le , I, IH, and Sd a
antigens. Manual tube, solid phase, or gel-column methods based on agglutina-
In contrast, antibodies occurring following immunization to tion of RBCs are the most common serologic assays performed in
protein antigens such as those in the Rh, Kell, Kidd, and Duffy blood transfusion medicine laboratories.